This study is led by Prof. Ying Li and Prof. Zuobin Zhu of Xuzhou Medical University, and Prof. Wenqiang Chang of Shandong University. A small molecule library consisting of 40 compounds, specifically N-substituted maleimide and its derivatives were initially screened in the study, which has been published in Mycology.

Among them, twelve maleimides, each with a distinct N-protection group, were synthesized using ring-opening and ring-closing reactions involving various amines and maleic anhydride. Additionally, a set of twenty-eight new Lamellarin analogs containing a maleimide ring structure were synthesized using an oxidative [3 + 2] cycloaddition aromatization cascade strategy. The compounds were screened to detect a novel maleimide analogue (MPD) with antifungal activity.
Subsequently, they analysed the safety of MPD, which has low toxicity to mammalian cell lines and is less likely to cause neurological damage and nephrotoxicity. The antifungal activity and safety of MPD supported further investigation of its antifungal mechanism.
Fungal cells
They found that there may be an effect of MPD on the iron ion homeostasis of fungal cells by the fact that MPD was more sensitive to the wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae knockout strain (aft2Δ). MPD did reduce intracellular iron levels in Candida albicans cells, as analysed by iron ion probe staining.
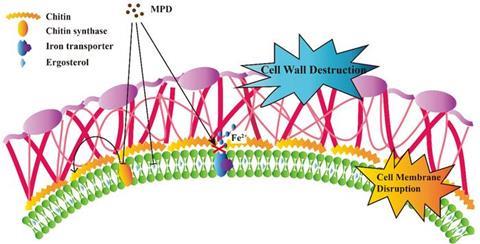
The decrease in iron concentration leads to a decrease in the synthesis of ergosterol, an important component of fungal cell membranes, which results in increased permeability and reduced flow ordering of fungal cell membranes. In this case, along with the leakage of intracellular trehalose, the fungal cells eventually die.
They also demonstrated the antifungal effect of MPD in vivo by using the Caenorhabditis elegans-Candida albicans infection model. The findings, therefore, demonstrate the efficacy of MPD as a novel antifungal compound, highlighting its potential as a promising option for the treatment of clinical candidiasis. The study also reveals the mechanism by which maleimide derivatives exert their antifungal effects.





No comments yet