One health
Communicable diseases remain one of the major causes of mortality worldwide. There are disparities in the numbers of individuals affected by disease between low-and-middle-income countries and those in developed nations. Microbes will play in important role in drug discovery: producing anticancer drugs and antimicrobials. Applying One Health principles, to understand the interaction of pathogens and the human host, development of diagnostics, treatments, and disease prevention, applied microbiologists can shape global health and wellbeing outcomes.
News
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce Covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
In a large, randomized trial, researchers have found that high-dose vitamin D3 did not reduce COVID-19 infection severity, but may impact long COVID outcomes.
Read story- News
Mothers' exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
A study dives into new depths to explore why only some babies develop severe infection to common bacteria. The research revealed that the babies that became most severely ill from E. coli infections also had markedly lower levels of germ-fighting antibodies transferred from their mothers.
- News
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
Reported adverse effects associated with the current first-line treatment for amoebiasis, coupled with the evolution of resistance to it, call for the need to search for plant-based alternatives. This study systematically reviews medicinal plants with activity against Entamoeba histolytica.
- News
Scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Researchers found that the Marburg virus, one of the world’s deadliest pathogens, is unusually efficient at getting inside human cells. They also showed that the virus’s entry protein contains structural features that explain this efficiency and point to a strategy for blocking infection.
More One Health
News
Everyday foods could hide fungal risks for mothers and children
A collaborative, multi-institutional project will examine how exposure to zearalenone – a mycoestrogen produced by mold with estrogen-like activity – may affect pregnancy outcomes and children’s growth.
- News
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Scientists have discovered that the aging gastrointestinal tract produces specific molecules that blunt the activity of a key gut-brain neuronal pathway, leading to age-related cognitive decline in mice.
- News
Research guides response to unprecedented 2023 E. coli outbreak affecting Calgary kids
Protocols developed by scientists informed care when hundreds of children were sick due to a severe strain of E. coli. Overall, 40 children were hospitalized, 21 developed HUS and nine required dialysis. The number of children who developed HUS was less than half of what would typically occur in an outbreak of this size.
- News
Ticks carrying more than one pathogen are on the rise in US Northeast
Tick-borne diseases are on the rise in the northeastern US, with many ticks carrying more than one pathogen. Most commonly found together were Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti. Co-infection with these two pathogens was more frequent than expected, approaching 11% by the end of the study.
- News
Webinar: Unraveling periprosthetic joint infection
The free ‘Unraveling Periprosthetic Joint Infection’ webinar on March 25 explores one of the most challenging complications in modern orthopedic medicine, sitting at the intersection of microbiology, surgery, and patient care.
- News
Severe COVID-19 and flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Severe COVID-19 and influenza infections prime the lungs for cancer and can accelerate the disease’s development, but vaccination heads off those harmful effects, new research indicates.
- News
Dengue vaccine remains 80.5% effective against severe cases after five years
The tetravalent dengue vaccine was 80.5% effective against severe dengue cases with warning signs over a five-year period. Overall, the vaccine was 65% effective in preventing symptomatic dengue (caused by any serotype) during the five years of monitoring.
- News
Researchers uncover how bacteria suppress immune defences in stubborn wound infections
A common bacterium can suppress the body’s early warning system in wounds, causing infections to persist and create an environment that allows other bacteria to take hold. Enterococcus faecalis releases large amounts of lactic acid in the wound, which lowers pH, weakens immune cells and prevents them from fighting an infection.
- News
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Scientists have uncovered a hidden link between gut health and the immune system, all thanks to a tiny island bird. They collected the poo of the Seychelles warbler to analyse their gut bacteria – and found that their immune genes influence which gut microbes thrive.
- News
Seaweed has the potential to create a shield to block norovirus infection
Seaweed has certain properties which have the ability to create a shield within the human body, effectively blocking norovirus infection. Fucoidan, from brown seaweed, showed the strongest and most consistent blocking activity against two major norovirus strains, GII.4 and GII.17.
- News
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Researchers have found strong links between a person’s history of antibiotic use and the composition of their gut microbiome, including the diversity of bacterial species.
- News
Low-cost preventive measures could mitigate spread of bacteria causing neonatal mortality
A new study found that a multifaceted infection prevention and control intervention could at least temporarily thwart outbreaks of infections from the Klebsiella pneumoniae bacterium.
- News
Specific gut bacteria species linked to muscle strength
A species of gut bacteria called Roseburia inulinivorans is specifically associated with human muscle strength and improved muscular performance in mice, finds new research. R inulinivorans changes certain metabolic processes in muscle, and converts muscle fibres to ‘fast-twitch’ (type II).
- News
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
A long-standing debate about the evolutionary origin of the world’s most widely cultivated ’magic mushroom’ – Psilocybe cubensis – may now have been settled. Scientists describe the discovery of a new species of magic mushroom from the grasslands of South Africa and Zimbabwe.
- News
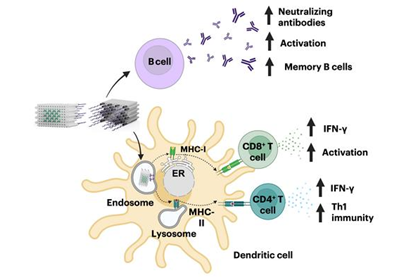
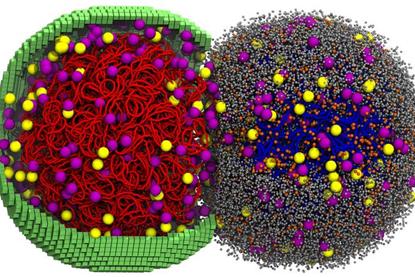
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Researchers have leveraged a recently developed highly versatile DNA origami nanotechnology that is both vaccine and adjuvant, named DoriVac, as an alternative to current vaccine platforms.
- News
Gut bacteria drive process that protects colon tissue
Researchers have shown that the identity of distinct regions of the colon are regulated by the gut microbiome. They identified nicotinic acid, a molecule produced by certain bacteria in the gut microbiome, as a main driver of these regional differences in the colon’s sections.
- News
Antibiotic resistance can vary depending on where the bacteria live
Antibiotic susceptibility in resistant bacteria is not static. New research shows that bacteria harbouring resistance genes may respond differently to antibiotics if they are tested under conditions other than those used in standard laboratory assays.
- News
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
By simulating the life cycle of a minimal bacterial cell — from DNA replication to protein translation to metabolism and cell division — scientists have opened a new frontier of computer vision into the essential processes of life.
- News
Stay or stray? Scientists discover why some gut microbes persist after fecal transplants
Scientists have identified why some gut microbes successfully stay in the gut after faecal transplants, whilst others are much more transient. They tracked key genetic features of gut bacteria in 86 healthy adults over the course of a year.