A therapy showing promise to help control tuberculosis (TB) does not interfere with combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), according to research by Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed).
“This is an important hurdle that this host-directed therapy had to clear in order to help patients battling both HIV and TB,” said Texas Biomed Professor Smriti Mehra, Ph.D., who led the study recently published in the peer-reviewed journal JCI Insight.
READ MORE: Study highlights factors associated with higher tuberculosis risk in South Africa
READ MORE: Researchers invent single, rapid test for both HIV and TB
TB is responsible for more than 1.3 million deaths worldwide every year. Dr. Mehra and her team have been investigating a therapy currently used in cancer as a potential treatment for patients with drug-resistant TB and/or comorbid HIV. While many cases of TB can be controlled with months of antibiotics, the infection can return in people who are immunocompromised as a result of HIV. Now that cART is so effective at controlling HIV, a resurging TB infection can often be deadly to those individuals.
Host-directed therapy
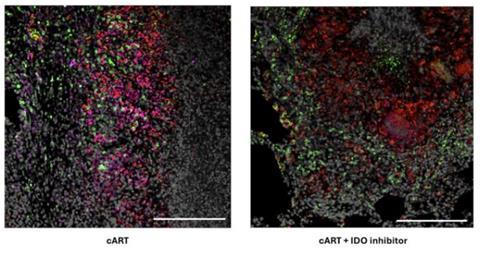
Dr. Mehra is studying a host-directed therapy that blocks or inhibits an immune system protein naturally found in the body. The protein, called IDO (short for Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase), normally suppresses the immune system, preventing it from causing excessive inflammation and organ damage. Inhibiting IDO for short intervals of time has led to more successful cancer treatments. Dr. Mehra’s team has previously shown the same approach improves control of TB in conjunction with antibiotics.
This current study in nonhuman primates with both TB and simian immunodeficiency virus, the nonhuman primate version of HIV, showed the IDO inhibitor does not interfere with cART.
“There was no increase in viral load in animals given cART and the IDO inhibitor, compared with animals only given cART, proving the inhibitor is safe to give to patients with HIV,” Dr. Mehra said.
Treatment regimen
Now that the researchers have shown the inhibitor works well in conjunction with TB antibiotics and with cART separately, they plan to study how it performs when given in conjunction with both antibiotics and cART together. This treatment regimen is standard for patients with both HIV and active TB. Dr. Mehra said that longer-term studies are also needed to confirm there are no unintended side effects.
The IDO inhibitor is already FDA-approved for use in patients with cancer, which shortens the path to potential approval for patients with TB/HIV when compared with developing a brand-new drug.







No comments yet