Cleveland Clinic researchers have used nanoparticles to develop a potential vaccine candidate against Dabie Bandavirus, formerly known as Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV), a tick-borne virus that currently has no prevention, treatment or cure.
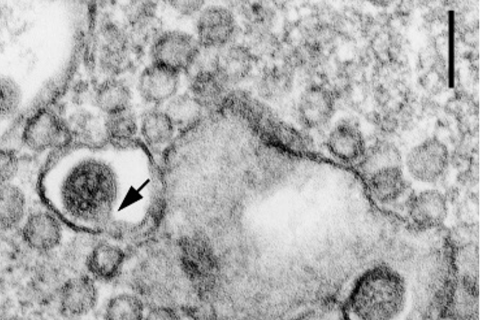
The patent-pending vaccine uses nanoparticles to carry the antigens that contain instructions for fighting off a virus. Nanoparticle vaccines are designed to effectively deliver antigens at a lower dose with fewer side effects for at-risk groups – including adults over age 50, who are the most vulnerable to SFTSV and the most susceptible to vaccine side effects.
The pre-clinical research, published in mBio, was led by Jae Jung, PhD, Director of Cleveland Clinic’s Sheikha Fatima bint Mubarak Global Center for Pathogen and Human Health Research.
“The Pathogen Center was founded to prepare for and protect against future global health crises before they start,” says Dr. Jung, who also serves as Department Chair of Cancer Biology and Director of Infection Biology. “There is already a desperate need for a SFTSV vaccine in Asia. Our goal was to develop one before it’s needed in America, too.”
Urgent research
The World Health Organization had declared SFTSV as needing “urgent research attention” several years ago, and it is still listed as a threat by the National Institutes of Health in the US. The virus spreads through the Asian longhorn tick, a species already present in 19 U.S. states including Ohio. It can also sometimes spread from human to human, mainly in a hospital setting.
Currently, physicians can only address the virus’s symptoms and keep infected patients hydrated and comfortable. While many people experience mild symptoms, adults over 50 years old can become severely ill and face a 30% mortality rate.
This same population unfortunately experiences certain vaccine side effects that typically don’t affect younger people.
Side effects
“We become more sensitive to certain vaccine side effects the older we get,” says study first author Dokyun (Leo) Kim. “We wanted to develop a treatment that’s age-dependent and can be given safely to the people who need it the most.”
Nanoparticle vaccines are promising for treating these at-risk groups because the antigens are bundled together, instead of free-floating throughout our bodies. Because our immune cells can find “bundles” of antigens on a nanoparticle more easily, the vaccine can be effective using a lower dose. When the vaccine dosage is reduced, its potential side effects are reduced as well, according to preliminary research conducted by Kim.
Dr. Jung’s lab hopes to test the SFTSV vaccine in humans next. And Kim says the possibilities don’t end there.
“We’re working to apply our nanoparticle technology to other viruses,” he says. “We have already developed a candidate for COVID-19, and we’re not stopping any time soon.”




No comments yet