Fonio (Digitaria exilis), a type of millet, is the oldest indigenous crop in West Africa and one of the fastest maturing cereals. Despite its low yield, the combination of quick maturation and drought tolerance and its ability to thrive in poor soils make it a useful model for understanding how cereals can adapt to future climate change conditions.

Nutritionally, fonio is comparable to other millets, says KAUST researcher Naheed Tabassum, but yields are much lower than the major cereal crops rice, maize and wheat. Tabassum believes fonio could complement staple crops amid climate change and desertification challenges.
Tabassum and colleagues, led by Heribert Hirt and Simon Krattinger, have investigated the potential to improve fonio by manipulating its association with soil microbes. Their research is published in Microbiome.
Arid conditions
Plants grown in arid conditions associate and interact with bacteria that help them combat abiotic challenges. Hirt and his group are experts on plant-microbe interactions and their role in plant growth and development, nutrient uptake and protection against biotic stress.
“Plants evolve in close interaction with microbial partners, which is crucial for their survival and fitness,” says Hirt. “As seeds are the bottleneck for vertical transmission (from the mother plant) of potentially beneficial microbial communities, we tried to unravel the role of the fonio seed microbiome in various abiotic conditions.”
Their study investigated the bacterial seed endophyte diversity in 126 fully sequenced genetic groups of fonio accessions from distinct locations in West Africa.
Endophytic bacteria
The role of endophytic bacteria in seeds has been linked to plant growth and protection, yet the specific mechanisms remain to be explained in detail. The results of this study suggest that seed-associated endophytes support plant growth promotion through nutrient availability and assimilation. Previous studies have shown that seed endophytes produce biocontrol inhibitors to protect from pathogens.
When they analyzed the seed microbiomes, the researchers found that fonio millet has diverse heritable seed endophytic taxa. “Despite finding diverse microbiomes in fonio from distinct geographical locations, all fonio plants share a set of microbes, a so-called core microbiome, which probably plays important functions in the general metabolism of this cereal,” says Hirt.
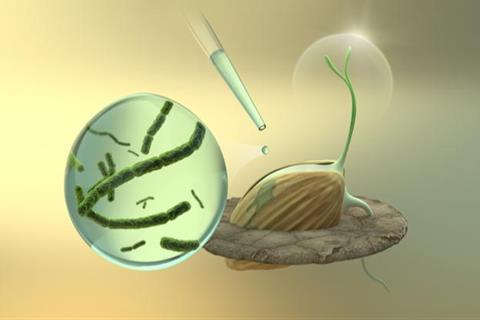
To test whether environmental factors influenced the composition of the seed microbiomes, the researchers gathered meteorological and soil data (precipitation, temperature, pH and soil structure) at the collection sites. They found a correlation between several of these parameters and microbial diversity, indicating that environmental factors may affect microbial composition and transgenerational transmission.
Distinct microhabitats
“The seed coat and storage tissue represent distinct microhabitats,” explains Tabassum. “The vertical transmission of microbiota to fortify the progeny of a plant species opens a new technological application in crop breeding.”
“Seed microbe engineering could be used for targeted metabolites or to produce antimicrobial compounds to improve plant biomass and yield under stresses,” she says.
The recently published study provides a proof of concept to explain the composition and diversity of the seed-associated microbiomes of fonio from a number of locations.
World first
In what they believe is a world first, the team performed genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of the 126 fonio accessions to identify genetic loci associated with seed endophyte diversity. This led to the identification of a number of known and novel genes that appear to influence the diversity of the microbial communities in different fonio accessions, suggesting that different fonio groups also genetically regulate the composition of their seed microbiomes.
“Although seed microbiome research is in its infancy, our work shows that it has great potential to advance our understanding of the plant-microbiome-environment interaction and in seed microbiome engineering of crops,” says Hirt.
“This study identified the seed microbiome as a potential target for enhancing crop resilience to climate stress in a sustainable way,” he concludes.




No comments yet