An international team of marine biogeochemist and atmospheric scientists have made a rare discovery in the almost uncharted atmosphere of the South Pacific Ocean. They found that nocturnal nanoparticle bursts that contain nitrogenous compounds originate when marine micro-organisms apparently shield themselves from UV radiation. These particles help form clouds over the ocean, which reduces warming of the climate.

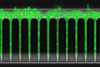
The study was performed in so-called air sea interface tank (ASIT) enclosures on the deck of a research vessel on several locations in the South Pacific Ocean. These simulated the local marine environment for three days in a row before the water in the enclosures was changed. Bursts of small particles were observed especially in the frontal water samples during the hours preceding dawn.
“Presumably they were from the marine organisms aiming to shield themselves from the upcoming harmful solar UV radiation. The observed particle formation was accompanied by signs of nitrogenous compounds, hinting at the origin of the observed nanoparticle bursts,” explains Associate Professor (tenure track) Matti Rissanen at Tampere University.
Demanding location
Observations from the remote South Pacific Ocean are rare because this isolated and wide open sea is a very for performing atmospheric measurements.
“These findings from the area are extremely important due to the scarceness of the observations and marine clouds being perhaps the biggest uncertainty relating to climate change predictions,” Rissanen adds.
Oceans absorb sunlight efficiently. A cloud cover on top of them reflects a significant portion of the light back into space. The birthing of clouds in these poorly measured regions remains particularly difficult to explain.
Important insight
”Our study sheds important insight into the underlying processes of particulate production above the ocean. The possible role of living organisms in these processes is particularly exciting,” says Siddharth Iyer, who works as an Academy Research Fellow at Tampere University.
The research article Evidence of nitrate-based nighttime atmospheric nucleation driven by marine microorganisms in the South Pacific was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The study was part of Matti Rissanen’s research that is funded by the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research.





No comments yet