All USA & Canada articles – Page 5
-
 News
NewsNew Arkansas Clean Plant Center partnership to boost Indian agriculture
The University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture has entered a five-year agreement with the Indian National Horticulture Board and Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare to help farmers in India improve agricultural production by limiting spread of pathogens.
-
 Opinion
OpinionWe couldn’t get people interested in science - until we started speaking their language
In 2020, Puerto Rico faced a misinformation crisis. Melanie Ortiz Alvarez De La Campa reveals how five STEM undergraduates created a sci-comm organization that helped pass legislation, educated thousands, and created an inclusive database of Caribbean scientists.
-
 News
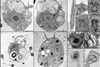
NewsClues to origins of complex life revealed with discovery of new unicellular organism and phylum
A new paper describes the discovery of Solarion arienae, a previously unknown unicellular organism that provides new insight into the earliest stages of complex life on Earth. This microscopic protist displays two distinct cell types and a unique predatory structure unlike any seen before.
-
 News
NewsNew vaccine against a deadly virus acts fast and protects for over a year
A research team has developed a vaccine made from a non-infectious version of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus that protects quickly and provides long-lasting immunity.
-
 News
NewsSoil carbon decomposition varies vastly, holding implications for climate models
A new study shows that even under uniform laboratory conditions, the rate of organic carbon decomposition in soil samples collected across the U.S. differed by up to tenfold, in part due to variations in soil mineral and microbial properties.
-
 News
NewsNew flu strain underscores urgent need for vigilance, vaccination, and investment in virus science
Virologists have issued a statement on the emergence of a new influenza A (H3N2) variant known as H3N2 subclade K that is spreading rapidly and may contribute to a more intense flu season worldwide. Public health agencies have reported sharp week-over-week increases in cases driven by this subclade.
-
 News
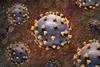
NewsScientists uncover how COVID-19 variants outsmart the immune system
Researchers have created the most comprehensive map to date showing how antibodies attach to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, and how viral mutations weaken that attachment.
-
 News
NewsTeam discovers cyanobacteria activate different genes by day and by night
By analyzing gene expression in the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme, scientists discovered that during daylight, the cells focus on metabolism. But under cover of darkness, they turn to the control of genome repair and activate various genetic elements.
-
 News
NewsGlobal Virus Network awards pandemic preparedness grants to advance global surveillance and early detection of viral threats
The Global Virus Network (GVN) is awarding pandemic preparedness research grants, totaling $160,000, to scientists across four continents, supporting innovative, investigator-led projects designed to enhance viral surveillance, early detection, and scientific preparedness.
-
 News
NewsResearchers subvert plasmids to combat antibiotic resistance
Scientists have devised a way to track the evolution and spread of antibiotic resistance in individual bacteria by measuring competition among plasmids. Plasmids evolve independently but also help drive bacterial evolution, including the development of resistance to antimicrobial compounds. They are the primary way that resistance can jump from one type of bacteria to another.
-
 News
NewsRebalancing lung repair with immune damage is key to surviving severe influenza
Recovery from deadly influenza infection may hinge on helping the lungs heal in addition to stopping the virus, according to a new study in mice, which shows that pairing modest antiviral therapies with immune modulation can restore damaged tissues and lung function, even after severe infection has taken hold.
-
 News
NewsScientists use computer model to improve hospitals’ ability to limit spread of drug-resistant infections
The computer model improves on traditional methods like contact tracing by inferring asymptomatic carriers in the spread of antibiotic-resistant infections.
-
 News
NewsDrinking water people believe to be safe and clean often contain potentially dangerous bacteria
A study in Guatemala found the sources of drinking water people believe to be safe and clean often contain potentially dangerous bacteria. Bottled water sold in large refillable jugs was the most frequently contaminated with coliform bacteria – an indicator of fecal contamination.
-
 News
NewsSmart toilet designs in Cambodia held promise, but a key piece was missing
A smart toilet design introduced in rural Cambodia was supposed to change lives—keeping families safe and protecting the environment. However, while households reported that they liked the new system, a crucial piece was missing: using it correctly.
-
 News
NewsStudy unveils structure, identification and characterization of the RibD-enolase complex in Francisella
A study aiming to identify anti-tularemia drug targets determined the atomic structure and identified its components of the native RibD-enolase protein complex in Francisella novicida.
-
 News
NewsMachine learning tool can scan for signs of extraterrestrial life
A machine learning framework can distinguish molecules made by biological processes from those formed through non-biological processes and could be used to analyze samples returned by current and future planetary missions.
-
 News
NewsProbiotic bifidobacterium may boost cancer treatment and suppress tumors
A new review explores how bifidobacterium, a common probiotic found in the gut, may contribute to cancer prevention and therapy. The authors highlight the growing importance of gut health in cancer treatment and shed light on how bifidobacterium could complement standard cancer therapies.
-
 News
NewsFlower to fruit: tracking the changing fungal community on blueberry plants
A study identifies how fungal diversity changes over time and across tissue types in highbush blueberry, revealing dynamic transitions in the phyllosphere from buds to ripe fruits. Early-season buds and flowers harbor the highest fungal diversity, while unripe green fruits display the lowest.
-
 News
NewsManure digesters on farms carry limited benefits and potential harms
Manure digesters, touted as eco-friendly solutions for managing agricultural waste and reducing greenhouse gases, have limited capacity to reduce livestock-related greenhouse gas emissions, and entail potential hazards that may outweigh their benefits.
-
 News
NewsScripps Research scientists receive $1.1 million to advance AI modeling for HIV vaccine development
Scripps Research scientists will purchase high-performance computing equipment to accelerate the identification of more effective HIV vaccine candidates through enhanced computational infrastructure, reduced data-processing bottlenecks, and state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
