All USA & Canada articles – Page 12
-
 News
NewsScientists reveals how tiny algae shaped the evolution of giant clams
Scientists have sequenced the genome of the most widespread species of giant clam, Tridacna maxima, to reveal how these creatures adapted their genome to coexist with algae living inside them.
-
 News
NewsFrom Fox News to MSNBC: Diverse media diet linked to higher trust in vaccines
People who get their news from an ideologically diverse array of sources are more likely to get vaccinated, regardless of their political affiliation, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsHigh uric acid levels - and harmful gut bacteria - linked to deadly outcomes in children with severe malaria
Researchers have uncovered a significant connection between elevated uric acid levels and life-threatening outcomes in children with severe malaria. The study identified hyperuricemia as a potential contributor to increased mortality and long-term neurodevelopmental challenges in children with severe malaria.
-
 Opinion
OpinionReproductive biology though the lens of the microbiome
Madangchanok Imchen and Seth R. Bordenstein from the One Health Microbiome Center - winner of AMI’s WH Pierce Prize 2024 - explore the potential of the reproductive microbiome, particularly the fascinating Wolbachia, to counter global disease threats.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop new weapon against harmful algal blooms
Few studies have looked into how algal biomass, especially cyanobacteria, can be used to create materials that remove phosphate from water. Now, researchers have transformed cyanobacterial biomass, which is typically a hazardous waste, into custom-made adsorbent materials that can pull harmful phosphorus out of water.
-
 News
NewsBacteria found to eat forever chemicals — and even some of their toxic byproducts
A new study shows that a strain taken from contaminated soil breaks apart the strong carbon-fluorine bonds of PFAS, as well as some of the shorter-chain PFAS left behind.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover unique microbes in Amazonian peatlands that could influence climate change
Researchers have identified an unknown family of microbes uniquely adapted to the waterlogged, low-oxygen conditions of tropical peatlands in Peru’s northwestern Amazonian rainforest.
-
 News
NewsA new vaccine approach could help combat future coronavirus pandemics
Researchers are able to create a mosaic nanoparticle vaccine - mosaic-8, based on the sarbecovirus receptor-binding proteins (RBDs), which would help combatting SARS-CoV-2 variants and other coronavirus subtypes.
-
 News
NewsNew study highlights role of lean red meat in gut and heart health as part of a balanced healthy diet
A research has suggested that a balanced and healthy dietary pattern that includes lean red meat has a beneficial role in gut microbiota changes and cardiovascular health.
-
 News
NewsThe secret ‘sex lives’ of bacteria: Study challenges old ideas about how species form
Researchers discovered that microbial species form and maintain their distinct identities through unique way of genetic material exchange, especially via homologous recombination, apart from the common asexual reproductive method.
-
 News
NewsUltrasensitive test detects, serially monitors intact virus levels in patients with COVID-19
A highly sensitive approach, adapted from cancer vesicles detection, was discovered to be able to detect SARS-CoV-2 viral particles in fluid samples of patients with acute COVID-19 infections.
-
 News
NewsHepatitis B is a problem for a growing number of patients on immunosuppressive medications
The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has unveiled an updated clinical practice guideline addressing the prevention and management of hepatitis B virus reactivation (HBVr) in patients on immunosuppressive drugs.
-
 News
NewsCuriosity-driven experiment helps unravel antibiotic-resistance mystery
An international collaboration has achieved an important breakthrough in understanding the genetic mechanisms that allow bacteria to build resistance to drugs.
-
 News
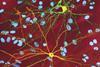
NewsAntiviral protein causes genetic changes implicated in Huntington’s disease progression
A new study shows APOBEC enzymes, which normally help fight viral infections by mutating viral DNA, are unusually active in the brains of Huntington’s patients.
-
 News
NewsNew study finds social programs could reduce the spread of HIV by 29%
Researchers have found that addressing barriers to HIV care from depression, homelessness, individual and neighborhood poverty, education disparities, lack of insurance and unemployment could reduce the national HIV incidence by 29% over 10 years.
-
 News
NewsLooking to Kenya’s Lake Victoria for what may come for Lake Erie
Scientists conducted a genetic survey on cyanobacteria in the Winam Gulf of Kenya’s Lake Victoria, which serves as a model for the cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms (cyanHABs) in Lake Erie under the warming climate.
-
 News
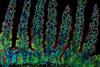
NewsNew research reveals how location influences how our immune system fights disease
Researchers have revealed how cells known as tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells play unique and specialized roles based on where they are located within the small intestine, providing a local first line of defense against re-infection.
-
 News
NewsNew paper creates roadmap for the next generation of bioelectronic medicine
A new paper offers a roadmap to the future of bioelectronic medicine — which makes use of electrical signals instead of drugs to diagnose and treat disease.
-
 News
NewsBiotin may shield brain from manganese-induced damage, study finds
New research showing the mechanisms by which manganese inflicts damage to the central nervous system suggests that the vitamin biotin - synthesized by gut bacteria - may have a protective effect, potentially mitigating manganese-induced damage.
-
 News
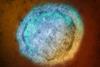
NewsScientists uncover structure of critical component in deadly Nipah virus
Through the structural and functional study of the deadly Nipah virus, a research team has identified a crucial viral component, viral polymerase complex, within its multiplication machinery, with which a part of the enzyme could potentially serve as a therapeutic target.
