All University of Michigan articles
-
 News
NewsHow can nursing homes protect more patients from infections?
New US national guidance calls for full-time infection prevention staff; more training, support and vaccination for all staff; and partnerships with hospitals and public health agencies.
-
 News
NewsExperts urge continued hepatitis B vaccine birth doses for newborns
In a new commentary, leading experts urge that all newborns in the United States continue to receive the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. Hepatitis B vaccines are safe and effective with over one billion doses administered worldwide.
-
 Careers
CareersSummer studentship: Amelia investigates how Streptococci aggregate with other oral bacteria
Amelia Rohim reports back on her AMI-sponsored summer studentship which focused on the investigation of inter-species aggregation between oral bacteria at the University of Michigan with Dr. Alexander Rickard.
-
 News
NewsGut infections often overlooked in men who have sex with men
It’s time to develop more effective ways to control and prevent sexually transmitted gut infections, urge the authors of an article that discusses discuss several sexually transmitted enteric pathogens that have become extremely multi-drug resistant.
-
 News
NewsBroad COVID-19 vaccination makes economic sense, especially for older adults, study finds
Vaccinating every person over 65 would actually save the U.S. money, while vaccinating all younger adults would be a reasonable investment, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsInappropriate prescriptions for antibiotics, glucocorticoids and opioids common at urgent cares
Urgent care visits commonly result in inappropriate prescriptions of antibiotics, glucocorticoids or opioids, researchers have warned.
-
 News
NewsStudy suggests some maternal HIV infections may be missed during pregnancy
Newborns exposed to HIV during pregnancy or birth should receive antiretroviral medication immediately after delivery - but a study finds more than half of infants diagnosed with HIV in their first year of life had not received this essential postnatal treatment.
-
 News
NewsSeasonal allergies caused by fungal spores now start three weeks earlier under climate change
Researchers have found that, on average, spore allergy season in the US was kicking off 22 days earlier in 2022 than it had been in 2003.
-
 News
NewsLiving near harmful algal blooms reduces life expectancy with ALS
Living close to cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms — which are present US-wide but are more common in coastal and Great Lake states — heightens the rate of dying from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, a study suggests.
-
 News
NewsResearchers engineer a herpes virus to turn on T cells for immunotherapy
Researchers have identified herpes virus saimiri, which infects the T cells of squirrel monkeys, as a source of proteins that activate pathways in T cells that are needed to promote T cell survival - a promising tool in the fight against cancer.
-
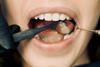 News
NewsMicrobial pioneers: how bacteria shape dental implant health from day one
A new study suggests that the earliest microbes to colonize a dental implant may determine its long-term fate. Using high-resolution genomic sequencing and a 12-week clinical timeline, scientists tracked how microbial ecosystems form around new dental implants.
-
 News
NewsBacterial villain behind Lake Erie’s ‘potent toxin’ unveiled by study
In Lake Erie, cyanobacteria can proliferate out of control, creating algal blooms that produce toxins that can harm wildlife and human health. Researchers have IDed the organism responsible for the toxins: a cyanobacteria called Dolichospermum.
-
 News
NewsInvesting in COVID-19 vaccination more than paid off for U.S., study finds
The US national Covid-19 vaccine strategy more than paid for itself after just one year, according to a new study. Because the vaccines reduced how many people developed serious illness or died, the nation saved more money than it spent.
-
 News
NewsA high-fat diet may impair response to infection
A new study in The Journal of Immunology reveals how a high-fat diet may impair the immune system’s ability to respond to infection by impacting the function of neutrophils, one of the first immune cells to respond to bacteria or viruses. The study demonstrated that male mice fed a high-fat ...
-
 News
NewsFewer than half of parents think they have accurate information about bird flu
Most parents say they don’t know if there have been cases of bird flu in their state, and less than half feel that they are able to find accurate and current information about it, according to a new national US poll.
-
 News
NewsLooking to Kenya’s Lake Victoria for what may come for Lake Erie
Scientists conducted a genetic survey on cyanobacteria in the Winam Gulf of Kenya’s Lake Victoria, which serves as a model for the cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms (cyanHABs) in Lake Erie under the warming climate.
-
 News
NewsExtreme rain heightens E. coli risks for communities of color in Texas
New research shows that communities of color in Texas face pronounced risks of E. coli exposure in nearby waters following storms that dump abnormally high amounts of rain.
-
 News
NewsBeach guardians: How hidden microbes protect coastal waters in a changing climate
Coastal water quality is closely impacted by the microbial compositions living in groundwater within beach sands due to the rising sea level, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how microbes create the most toxic form of mercury
Mercury is extraordinarily toxic, but it becomes especially dangerous when transformed into methylmercury – a form so harmful that just a few billionths of a gram can cause severe and lasting neurological damage to a developing fetus. Unfortunately, methylmercury often makes its way into our bodies through seafood – but ...
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria engineered to act as tumor GPS for immunotherapies
Cancer researchers have engineered gut derived E. coli bacteria to express immune-activating cytokines on their surfaces, with the idea that the bacteria would move into tumors and induce potent immune responses.
