Clean water
UNICEF estimates that over 2.2 billion people worldwide do not have access to clean drinking water. Micro-organisms are responsible for a host of waterborne diseases, but simultaneously offer solutions in purifying water and improving sanitation. Biofertilizers offer promising solutions for reduced nutrient runoff and wastewater recycling. As well as applying microbes to combat the problem, applied microbiologists can use their knowledge of health and disease to reduce cases of waterborne disease.
News
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
Reported adverse effects associated with the current first-line treatment for amoebiasis, coupled with the evolution of resistance to it, call for the need to search for plant-based alternatives. This study systematically reviews medicinal plants with activity against Entamoeba histolytica.
Read story- News
Tiny plastics, green solutions: How algae could help clean polluted waters
A new review examines how algae interact with microplastics in aquatic systems. Importantly, it highlights how their biological interactions could be harnessed to mitigate microplastic pollution, offering new perspectives for sustainable aquatic environmental management.
- News
Diisobutyl phthalate at environmental concentration promotes conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes
Researchers investigating the ecological safety risks posed by dibutyl phthalate (DBP), in aquatic environments found it significantly increased conjugative transfer frequency in both intragenus (E. coli DH5α to E. coli HB101) and intergenus (E. coli DH5α to B. subtilis WB100N) systems.
- News
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Researchers investigated how the upgrade of a WWTP influenced nitrogen-cycling microorganisms and DNA viruses in its receiving river. The research compared the river whose WWTP was upgraded during the study period against the river whose upgrade occurred prior to the study.
More Clean water
News
Periphyton closes the nitrogen budget gap in rice paddies
Scientists identify a previously overlooked microbial N sink in rice paddies. Periphyton, a thin microbial community that develops at the soil–water interface, is composed of algae, bacteria, and extracellular polymeric substances, forming a dense microhabitat with strong capacities for nutrient uptake, transformation, and temporary storage.
More clean water
- News
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
A new review explores how technologies using electricity-generating bacteria—like those already piloted at the UK’s Glastonbury Festival and in field trials in Uganda, Kenya, and South Africa—could help us reclaim resources currently being flushed away.
- News
Scientists unlock magnetic secrets of bacteria with built-in compass
Some bacteria are miniature masters of navigation: A built-in “compass” made of magnetic nanoparticles helps them to reliably find the optimal habitat. Researchers have now unlocked the magnetic properties of individual bacteria — an important step toward harnessing the potential for technology.
- News
World Water Day 2026: Book your free place on our Gender Equality and Water webinar
Applied Microbiology International will hold a free webinar on ‘Gender Equality and Water’ to mark World Water Day 2026 - March 18 2026. We’ll be joined by Professor Jiménez Cisneros, an expert in water management, sanitation and sustainable development, and Professor Lyla Mehta, an expert on water, sanitation, gender and development.
- News
Elevated E. coli, staph still detected in Potomac river 4 weeks after sewage spill
Nearly a month after a wastewater pipe broke and spewed hundreds of millions of gallons of raw sewage into the Potomac River just north of Washington, D.C., the latest water testing results continue to show high levels of E. coli and S. aureus, including antibiotic-resistant MRSA.
- News
Lower tillage boosts the soil’s natural phosphorus cycle - cutting the need for costly fertilizer inputs
Long-term tillage reduction helps to restore the soil’s natural phosphorus cycle, supporting more sustainable nutrient management with less reliance on costly and finite fertilizer inputs, according to a new study published in Sustainable Microbiology.
- News
Strategic changes in water treatment could prevent disease outbreaks
A breakthrough new study shows how strategic changes in water treatment effectively treated a deadly outbreak of Legionnaires’ Disease. For the first time, the study provides evidence of an outbreak being stopped by introducing disinfection to previously untreated groundwater.
- News
Team finds E. coli, other pathogens in Potomac River after sewage spill
Following one of the largest sewage spills in U.S. history, researchers detected high levels of fecal-related bacteria and disease-causing pathogens in the Potomac River, raising urgent public health concerns and underscoring the risks posed by aging sewer infrastructure.
- News
Large-scale study analyses the impact of climate on Legionnaires’ disease in Catalonia
A study has analysed the relationship between climatic conditions, the presence of Legionella in water systems and cases of Legionnaires’ disease in Catalonia. The link between these different factors highlights the need to adapt prevention and surveillance strategies in the context of climate change.
- News
CARB-X to support development of typhoid fever diagnostic from Chembio
CARB-X is awarding US$1.8 million to Chembio Diagnostic Systems, Inc. to develop a rapid point-of-care test for the detection of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies to diagnose acute infection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.
- News
Previously unknown viruses discovered in groundwater
Researchers have created a comprehensive picture of viral diversity and function in a groundwater system. They identified over 257,000 viral operational taxonomic units, i.e. viruses at species level, 99 % of which were previously unknown.
- News
Genes from corn’s wild ancestor change soil microbial community, improve sustainability
Corn bred with genes from wild relatives can reshape soil microbial communities and reduce nitrogen loss — with no yield reduction, according to new research. It’s the first time corn’s genetic makeup has been linked with inhibition of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria.
- News
Lab-grown algae removes microplastics from water
Scientists have applied a revolutionary strain of algae toward capturing and removing harmful microplastics from polluted water. The aim is to repurpose the collected microplastics into safe, bioplastic products such as composite plastic films.
- News
Researchers uncover the invisible worlds beneath our feet
An analysis of a natural aquifer revealed that despite their close spatial contact and possible interactions, the microorganisms in the water and on the rock form two strongly contrasting ecological communities.
- News
Researchers uncover hidden toxin risks during nutrient-starved algal blooms
Researchers have shown that extended nutrient deprivation can significantly increase toxin content per cell in the benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima, even when cell numbers remain relatively stable. Toxin risk may increase quietly under nutrient-poor conditions without obvious bloom expansion.
- News
Machine learning reveals how to maximize biochar yield from algae
Researchers have developed a powerful machine learning framework that can accurately predict and optimize biochar production from algae, offering a faster and more sustainable path toward carbon rich materials for climate mitigation, soil improvement, and environmental applications.
- News
£2.8 million research project to combat one of the world’s most urgent health threats
An ambitious new £2.8 million international programme will aim to tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR) across East Africa. It will examine how environmental, social and economic factors influence the spread of drug-resistant infections in East African communities.
- News
Student focused on pathogens says new award has opened a door to span aquaculture and ecology
A University of Stirling student who is the latest recipient of the Nikos Steiropoulos Aquaculture Scholarship from MSD Animal Health UK says the award has helped to “open a door she could only have dreamed of”.
- News
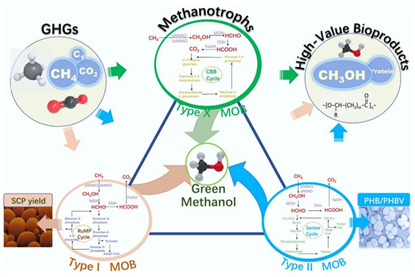
Methane eating microbes turn a powerful greenhouse gas into green plastics, feed, and fuel
Methane eating microbes could help turn a powerful greenhouse gas into everyday products like animal feed, green plastics, and cleaner fuels, according to a new scientific review of fast moving research on these unusual bacteria.