All Research News articles – Page 32
-
 News
NewsCovid-19 virus can damage the retina - even without severe respiratory disease
An experimental study in mice shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection can damage the retinas, with long-term implications for vision.
-
 News
NewsThe viral puzzle of why humans are susceptible to hepatitis B - but monkeys are not
Scientists collaborated to reveal the structural features of hepatitis B viral receptor homologue in macaques that restrict viral entry into their cells.
-
 News
NewsFungal structures could be deployed in aerospace industry
Manufacturing a material that mimics mushrooms and other fungal structures could provide opportunities in any number of areas, ranging from aerospace engineering to clothing production.
-
 News
NewsStudy untangles how COVID-19 wreaks widespread damage in the body
A new study sheds light on the pathways that drive organ damage and death in severe COVID-19 and helps explain why survivors of the disease can experience long-term complications.
-
 News
NewsPeat-bog fungi produce substances that kill tuberculosis-causing bacteria
An analysis of fungi collected from peat bogs has identified several species that produce substances toxic to the bacterium that causes the human disease tuberculosis.
-
 News
NewsBiohybrid of fungus and wood produces bioluminescent hardwood
Researchers are currently pursuing an idea for a new type of composite material based on hardwood: luminous wood.
-
 News
NewsPregnancy enhances natural immunity to block severe flu
Scientists discover a natural flu defense mechanism that activates in the nasal cavity during pregnancy.
-
 News
NewsHow did human brains get so big? The answer could be in our gut
Microbes supporting the production of more metabolic energy could be key to the evolution of large brains, according to a study that shows gut microbes from different animal species shape variations in their biology.
-
 News
NewsGlobal review charts lethal impact of fungal infection after lung disease
An international study of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis revealed that around 32% of people who have had prior damage from lung diseases will die after five years if they also get a common fungal infection.
-
 News
NewsSatellite evidence bolsters case that climate change caused mass elephant die-off
New analysis showing carcass distribution and algae in watering holes points to climate-induced poisoning of over 300 African elephants.
-
 News
NewsCold plasma isn’t just for sterilisation - it could become a vital green tool in water purification
Cold plasma isn’t just for sterilisation, but offers potential as a sustainable water treatment that can target stubborn contaminants like biofilms and pharmaceuticals, according to a new review.
-
 News
NewsBacteria ditch tags to dodge antibiotics
Bacteria modify their ribosomes when exposed to widely used antibiotics, according to new research. The subtle changes might be enough to alter the binding site of drug targets and constitute a possible new mechanism of antibiotic resistance.
-
 News
NewsA new approach to predicting malaria drug resistance
Researchers analyzed the genomes of hundreds of malaria parasites to determine which genetic variants are most likely to confer drug resistance.
-
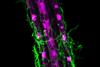 News
NewsNew study discovers the mechanism for fungal colonization of plant roots
Scientists have discovered how the beneficial root fungus Serendipita indica successfully colonizes plant roots of the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana.
-
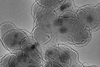 News
NewsNewly designed nanomaterial shows promise as antimicrobial agent
Newly developed nanocrystals show potential as antimicrobial agents that are stable, effective and easy to produce.
-
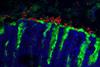 News
NewsMouse gut fungus reveals secrets of symbiosis and allergy
A fungus discovered in the mouse stomach may hold a key to fungal evolution within the gastrointestinal tract, according to new research. The finding suggests that preclinical studies until now have overlooked a major influencer of mouse physiology.
-
 News
NewsOceans emit sulfur and cool the climate more than previously thought
Researchers have quantified for the first time the global emissions of a sulfur gas produced by plankton, revealing it cools the climate more than previously thought, especially over the Southern Ocean.
-
 News
NewsCervical cancer deaths in young women plummet after introduction of HPV vaccine
Cervical cancer deaths have plunged dramatically among women under age 25, and researchers believe this is likely due to HPV vaccination.
-
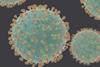 News
NewsResearchers develop lysosomal TRAP for clearance of viruses and variants
Researchers have developed a novel lysosomal strategy for clearing viruses and their variants. This lysosomal ‘TRAP’ (lysoTRAP) shows potential for inhibiting infection by viruses and variants in cell, mouse, hamster, and human lung organoid models.
-
 News
NewsZoonotic transmission of Covid has led to infections in more than 30 mammalian species
Zoonotic transmission of severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has been found to result in infections in more than 30 mammalian species, according to a study published in Zoonoses journal.
