
Linda Stewart
News and Current Affairs Editor
Linda studied Pure & Applied Biology BA at St Anne’s College, Oxford, before completing an MSc in Conservation at UCL. After two years in a Water Service lab in Northern Ireland, she switched to a career in newspaper journalism, working as a general reporter at the Belfast Telegraph before becoming the regional daily’s first Environment Correspondent from 2008 until 2016. She was named Environment Correspondent of the Year 2011 and Feature Journalist of the Year in 2014 at the NI Media Awards. After serving as editor on a number of retail sector magazines, she is enjoying turning her journalism skills to delivering fresh and fascinating scientific news content in The Microbiologist.
Contact info
 News
NewsBacteria breakthrough could accelerate mosquito control schemes
Mosquito larvae grow faster if they’re exposed to particular bacteria, according to a new study that could help global health programmes.
 News
NewsScientists examine how wastewater practices in Florida Keys impact water quality
A new study has tracked how wastewater nutrients migrate from disposal sites in the Florida Keys, and the results have already informed wastewater practices in the region.
 News
NewsNew findings on animal viruses with potential to infect humans
Scientists investigating animal viruses with potential to infect humans have identified a critical protein that could enable spillover of a family of organisms called arteriviruses.
 News
NewsEnhanced screening methods prevent spread of drug-resistant fungal infections in hospitals
Researchers have enhanced hospital screening protocols for Candida auris, an often drug-resistant fungal pathogen. These new guidelines could promote early detection of the harmful fungus in high-risk patients and prevent hospital outbreaks.
 News
NewsWater fern offers safe potential global food insecurity solution - with no cyanotoxins
An international effort to test Azolla found that it does not contain cyanotoxins, potent toxins produced by a type of cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae, associated with the plant.
 News
NewsStudy sheds light on increased rates of severe human infections caused by Streptococcus subspecies
An increase in rates of severe invasive infections becoming resistant to key antibiotics has a team of infectious disease researchers studying a recently emerged strain of bacteria called Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis (SDSE).
 News
NewsTrial of rectal microbicide for HIV prevention begins in US
A clinical trial has launched to examine the safety and acceptability of a novel rectal HIV microbicide douche containing the antiretroviral drug tenofovir.
 News
NewsHistones show promise against bacterial infections
Scientists have outlined that human histones have antimicrobial activity against different bacteria, including biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, one of the six most resistant bacteria in the world.
 News
NewsExperts recommend considering dietary factors in probiotics and prebiotics research
A new Perspective paper finds that, while diet is a major determinant of gut microbiome composition and function, it has rarely been incorporated as a variable in research on the efficacy of probiotics and prebiotics.
 News
NewsAI tackles huge problem of antimicrobial resistance in intensive care
Artificial intelligence (AI) can provide same-day assessments of antimicrobial resistance for patients in intensive care – critical to preventing life-threatening sepsis.
 News
NewsInfant gut microbiota development predicts future health
Infants’ gut microbiota development follows one of five predictable trajectories, significantly influenced by infant exposures, according to a new study. These are strong indicators of later health outcomes, including allergies, growth patterns, and infections.
 News
NewsA lung pathogen’s dilemma: infect or resist antibiotics?
Research has uncovered how Pseudomonas aeruginosa manages the trade-off between colonizing and surviving during infection by switching between biofilm formation for antibiotic protection and a more mobile, “planktonic” state to spread and access nutrients.
 News
NewsGut bacteria transfer genes to disable weapons of their competitors
New research shows how common gut bacteria tame their antagonistic neighbors by transferring genes that change their weapon systems.
 News
NewsBeneficial gut microbe has surprising metabolic capabilities
To address childhood malnutrition — which affects 200 million children globally — researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis developed a therapeutic food that nourishes the collections of beneficial microbes that reside in the gut, and improves children’s growth and other measures of their health.
 News
NewsBacteria and fungi found on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
Bacteria and fungi from the wings of bats could play a significant role in saving them from white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fungal disease affecting the skin of wings and muzzle, which has nearly wiped out vulnerable bat populations across North America.
 News
NewsA metabolic secret of ethane-consuming archaea unraveled
Scientists have presented a study on the degradation of ethane, the second most abundant alkane in seeps on the deep seafloor. They characterized enzymes involved in the process and found that their reaction breaks an established dogma in the field of anaerobic biochemistry.
 News
NewsLyme borreliosis: New approach for developing targeted therapy
A research team has made significant progress in understanding the mechanism of Lyme borreliosis infection and identified a potential way forward for the development of targeted therapies that do not rely on antibiotics.
 News
NewsUnnoticeable electric currents could reduce skin infections
Using a few zaps of electricity to the skin, researchers can stop bacterial infections without using any drugs. For the first time, researchers have designed a skin patch that uses imperceptible electric currents to control microbes.
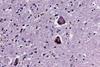 News
NewsAntibiotics and antifungals may slightly affect Parkinson’s risk, study finds
A study has found that people who took multiple courses of penicillin antibiotics had a modestly lower risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, a surprising finding that researchers say highlights the complex relationship between bacteria in the digestive tract and brain health.
 News
NewsNative fungus could offer biocontrol for invasive autumn olive
Researchers are studying a native fungus that potentially could kill the invasive autumn olive with minimal human interaction.To remove the autumn olive currently, the plant needs to have its underground root system removed in addition to the destruction of the plant itself, but this fungus could make this process much easier.

