Latest news
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Scientists have uncovered a hidden link between gut health and the immune system, all thanks to a tiny island bird. They collected the poo of the Seychelles warbler to analyse their gut bacteria – and found that their immune genes influence which gut microbes thrive.
Seaweed has the potential to create a shield to block norovirus infection
Seaweed has certain properties which have the ability to create a shield within the human body, effectively blocking norovirus infection. Fucoidan, from brown seaweed, showed the strongest and most consistent blocking activity against two major norovirus strains, GII.4 and GII.17.
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Researchers have found strong links between a person’s history of antibiotic use and the composition of their gut microbiome, including the diversity of bacterial species.
Low-cost preventive measures could mitigate spread of bacteria causing neonatal mortality
A new study found that a multifaceted infection prevention and control intervention could at least temporarily thwart outbreaks of infections from the Klebsiella pneumoniae bacterium.
Specific gut bacteria species linked to muscle strength
A species of gut bacteria called Roseburia inulinivorans is specifically associated with human muscle strength and improved muscular performance in mice, finds new research. R inulinivorans changes certain metabolic processes in muscle, and converts muscle fibres to ‘fast-twitch’ (type II).
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
A long-standing debate about the evolutionary origin of the world’s most widely cultivated ’magic mushroom’ – Psilocybe cubensis – may now have been settled. Scientists describe the discovery of a new species of magic mushroom from the grasslands of South Africa and Zimbabwe.
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Scientists have uncovered a hidden link between gut health and the immune system, all thanks to a tiny island bird. They collected the poo of the Seychelles warbler to analyse their gut bacteria – and found that their immune genes influence which gut microbes thrive.
Seaweed has the potential to create a shield to block norovirus infection
Seaweed has certain properties which have the ability to create a shield within the human body, effectively blocking norovirus infection. Fucoidan, from brown seaweed, showed the strongest and most consistent blocking activity against two major norovirus strains, GII.4 and GII.17.
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Researchers have found strong links between a person’s history of antibiotic use and the composition of their gut microbiome, including the diversity of bacterial species.
EnteroBiotix announces completion of enrolment in Phase 2a Trial evaluating EBX-102-02 prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation
EnteroBiotix announced that the investigator-initiated Phase 2a MAST trial has completed its enrolment of 50 adult patients undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) for defined haematological malignancies.
Thermo Fisher Scientific launches new color-based culture media to help detect Candida infections faster
Thermo Fisher Scientific today announced the launch of Thermo Scientific™ Brilliance™ Candida 2 Agar and Spectra™ Candida Agar, new color-based (chromogenic) culture media to help laboratories quickly detect and differentiate clinically important Candida species.
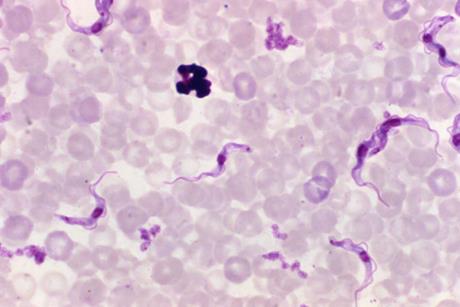
Acoziborole Winthrop receives European Medicines Agency positive opinion as three-tablet, single-dose treatment for most common form of sleeping sickness
The European Medicines Agency has granted a positive opinion to Acoziborole Winthrop (acoziborole) as a single-dose oral treatment for both early- and advanced-stage gambiense sleeping sickness in adults as well as in adolescents 12 years and older weighing at least 40 kilograms.
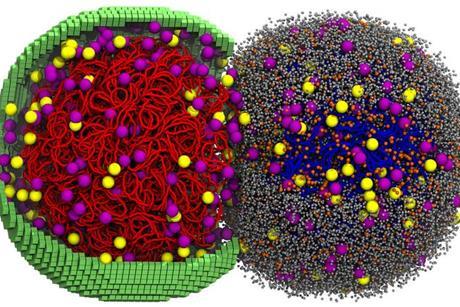
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
By simulating the life cycle of a minimal bacterial cell — from DNA replication to protein translation to metabolism and cell division — scientists have opened a new frontier of computer vision into the essential processes of life.
‘Bugs delivering drugs’ – new approach to colorectal cancer treatment using common food-borne bacteria
Researchers have published a novel approach to fight colorectal cancer, using modified bacteria as a courier to deliver potent cancer-killing proteins into tumor cells.
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
An antibody test for the infectious disease Mpox was successfully developed during the new clade 1b outbreak in Rwanda, the first time that an assay of its kind has been validated within this setting.
From microbial processes to biofilm control: our interview with JAM Microbial Biotechnology lead editor Manuel Simões
Professor Manuel Simões, Deputy Editor of the Journal of Applied Microbiology, has just been appointed as the journal’s new lead editor in Microbial Biotechnology. Here’s why he’s looking forward to the challenge.
Growing buildings in space: researchers test fungi as construction material for moon, Mars
A NASA-funded project will investigate whether certain fungi can be combined with regolith — loose rock and soil found on the surface of the moon and other planets — to create materials that could one day support construction in places other than Earth.
Under the Lens: Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
The latest episode of Applied Microbiology International’s ‘Under The Lens’ video series turns the spotlight on the contentious issue of raw milk, with AMI Trustee Professor Emmanuel Adukwu interviewing Professor Nicola Holden and Dr Gil Domingue.