More News – Page 96
-
 News
NewsInfection ability of viruses reduced by 96% using mechanical methods
An international research project in which the URV has taken part has designed and manufactured a surface that has virucidal properties but does not use any chemicals.
-
 News
NewsSwitching to vegan or ketogenic diet rapidly impacts immune system - and gut microbiome
A study found that switching to a vegan diet prompted responses linked to innate immunity, while the keto diet elicited responses associated with adaptive immunity, along with metabolic changes and shifts in the gut microbiomes.
-
 News
NewsResin destroys coronavirus from plastic surfaces
A recent study found that a resin ingredient is effective against coronaviruses and strongly decreases their infectivity on plastic surfaces.
-
 News
NewsLifetime of ‘biodegradable’ straws in the ocean is 8-20 months, study finds
Researchers found that some commercial bioplastic or paper straws might disintegrate within eight to 20 months in coastal ocean systems and switching to foam makes a major difference.
-
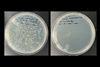 News
NewsAntiviral color nanocoating technology that actually works
Scientists have developed a nanocoating technology that not only maximizes the antiviral activity of the surface, but also enables the realization of various colors.
-
 News
NewsBIPOC individuals bear greater post-COVID burdens
In a study, black and multiracial participants reported more days of lost work and health aftereffects when compared with white participants.
-
 News
NewsIncreased hygiene during pandemic may have curbed development of immunity in children
Increased hygiene during the pandemic reduced microbial diversity in daycare settings - and this may have affected development of immunity against non-communicable diseases in children by limiting exposure to diverse microbes.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiota influence severity of respiratory viral infection
The composition of microbiota found in the gut influences how susceptible mice are to respiratory virus infections and the severity of these infections, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsTomato juice’s antimicrobial properties can kill salmonella
Tomato juice can kill Salmonella typhi and other bacteria that can harm people’s digestive and urinary tract health.
-
 News
NewsDNA particles that mimic viruses hold promise as vaccines
Using a DNA-based scaffold carrying viral proteins, researchers created a vaccine that provokes a strong antibody response against SARS-CoV-2.
-
 News
NewsProbiotics promote weight loss in obese dogs
Researchers have identified two strains of probiotics that can be used to reduce weight in obese dogs.
-
 News
NewsNitrogen-based fertilizers differentially affect protist community composition in paddy field soils
New research investigating the differential effects of nitrogen fertilizer types on paddy field protist communities showed that predatory protists were the major functional and most sensitive group to nitrogen fertilizers.
-
 News
News Real life data reveals success in controlling respiratory syncytial virus
Early data after passive immunisation with a monoclonal antibody against severe respiratory syncytial virus in 2023 show a decline in hospitalisations and length of stay especially in the most vulnerable group of infants under the age of six months.
-
 News
NewsViral protein fragments may unlock mystery behind serious COVID-19 outcomes
‘Zombie’ virus fragments continue to cause inflammation after the virus is destroyed, a new study finds.
-
 News
NewsRising sea levels could lead to more methane emitted from wetlands
A low-salinity Bay Area estuary ecosystem is producing higher-than-expected levels of methane.
-
 News
NewsResearchers control biofilm formation using optical traps
As a precise tool for influencing biofilm growth patterns, laser manipulation could enable biofilms to be used for sensors and more.
-
 News
NewsUnconventional yeast boosts quality of carbonic maceration wine, rosé wine and orange wine
A new study finds that this yeast speeds up the winemaking process and improves the organoleptic properties of wines.
-
 News
NewsResearchers create safer form of Coxiella burnetii for scientific use
Scientists have unexpectedly discovered that the weakened form of the bacteria Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii) not typically known to cause disease, has naturally acquired an ability to do so.
-
 News
NewsStatistics give a chance to prevent river tragedies like the Oder River crisis
Researchers believe there is a possibility of avoiding fish kills like the one in the Oder River in summer 2022, which was caused by the abrupt proliferation of golden algae, triggered by a combination of various factors. But it requires a change in the approach to analyzing parameters recorded at river monitoring stations.
-
 News
NewsSimulations show how HIV sneaks into the nucleus of the cell
A new study has revealed how HIV squirms its way into the nucleus as it invades a cell.

