More News – Page 80
-
 News
NewsHost’s sex plays key role in how gut microbiome evolves with age
Researchers studied how aging affects gut bacteria in a special group of rats generated to have genetic diversity similar to humans. Their research found that both biological sex and mitochondrial DNA—the small set of genes inherited only from mothers—play a key role in how gut bacteria change over time.
-
 News
NewsDigging into the world of plant-growth-promoting microbes
A team including members of AMI has provided a model illustrating how Pseudomonas bacteria can influence root development to promote growth and enhance the adaptation of plants under salinity stress.
-
 News
NewsLead science organizations affirm vaccine safety amid rising misinformation and declining trust
A unified statement, issued by a coalition of leading scientific and medical organizations, addresses the rise in vaccine misinformation and a decline in trust of science, amidst the outbreaks of preventible infectious diseases. It reassures the current concerns on vaccine safety and emphasizes the importance of vaccinations in public health.
-
 News
NewsLeafcutter ants recognize and fight pathogen with social immunity
Various characteristics of social immune memory were observed in colonies of Atta sexdens (lemon leafcutter ants) exposed to different pathogenic fungi. Such information is useful for future development of appropriate pest control.
-
 News
NewsPlastic-degrading enzymes from landfills
Researchers identified and analysed the structure and predicted functions of potential plastic-degrading enzymes in collected landfills sample from around the world, in an effort to reduce plastic pollution.
-
 News
NewsFDA-approved dialysis drug may help fight against antimicrobial resistance
In account of the imminent threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a study revealed that the FDA-approved sevelamer, which is used to treat chronic kidney disease undergoing dialysis, is successful in the removal of other off-target antibiotics (vancomycin and daptomycin) from the gut.
-
 News
NewsProfessor Sabiha Essack wins Christiana Figueres Policy to Practice Award
Professor Sabiha Essack, the South African Research Chair in Antibiotic Resistance and One Health, Professor in Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of KwaZulu-Natal, has been awarded the Christiana Figueres Policy to Practice Award.
-
 News
NewsAfro-Caribbean Commercial Science Network (ACCSN) named as winner of Dorothy Jones Diversity and Inclusion Achievement Award 2024
The Afro-Caribbean Commercial Science Network (ACCSN), founded by Daniel Similaki, has been named as this year’s winner of the Dorothy Jones Diversity and Inclusion Achievement Award 2024.
-
 News
NewsRed coral colonies survive a decade after being transplanted in the Medes Islands
The red coral colonies that were transplanted a decade ago on the seabed of the Medes Islands have survived successfully. They are very similar to the original communities and have contributed to the recovery of the functioning of the coral reef.
-
 News
NewsBacteria invade brain after implanting medical devices
Researchers have discovered that bacteria can invade the brain after a medical device is implanted, contributing to inflammation and reducing the device’s long-term effectiveness.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover protein key to bacteria’s survival in extreme environments
A new discovery sheds light on how certain bacteria – including strains that cause food poisoning and anthrax – form spores for survival.
-
 News
NewsRice research team creates universal RNA barcoding system for tracking gene transfer in bacteria
An interdisciplinary group of researchers at Rice University has developed an innovative RNA “barcoding” method to track gene transfer in microbial communities, providing new insights into how genes move across species.
-
 News
NewsNew ‘shy’ fungus found in old-growth forest
Although fungi of the genus Piloderma are common, scientists have now discovered five previously unknown species. One of these is one of the most widely distributed species in Northern Europe, while another is found only in old-growth forests.
-
 News
NewsImmature platelet fraction offers clinical predictor for enhanced platelet recovery in patients with dengue fever
Immature platelet fraction (IPF) is recognized as a marker for thrombopoiesis, but a new study indicates that IPF% can be utilized as a predictor of platelet increase in patients with dengue infection.
-
 News
NewsTunnel-building virus: How Zika transmits from mother to fetus
For the first time, researchers demonstrated the component involved in the tunneling nanotubes built by Zika virus to infect placental cells, an infection mechanism which is unique to the Zika virus alone.
-
 News
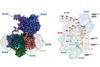
NewsWithout oxygen: How primordial microbes breathed
Scientists decode the fundamental mechanisms of a cell respiratory enzyme in ancient bacterial cells, with potential applications in removing greenhouse gases and drug development against pathogens.
-
 News
NewsNewly identified bacterial protein helps design cancer drug delivery system
Researchers have identified a previously unknown bacterial protein, the unique structure of which acts as an actin homolog that can be used to design protein nanoparticles for the targeted delivery of anticancer drugs to tumors.
-
 News
NewsResearchers demonstrate new technique for boosting plant growth with bacteria
A single combined delivery system incorporating multiple active ingredients, including plant growth-promoting bacteria and agrochemicals, is developed to ensure beneficial bacterial survival and improve plant growths.
-
 News
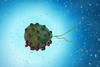
NewsMagnetic microalgae on a mission to become robots
A team of researchers has developed a green algae-based biohybrid micro swimmer covered with magnetic material, whose swimming ability is largely unaffected by the coating.
-
 News
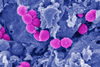
NewsResearch uncovers new strategy to reduce tissue damage from flesh-eating bacteria
A new study reveals a novel approach to mitigating tissue damage caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, the flesh-eating bacterium responsible for severe infections such as necrotizing fasciitis.
