More News – Page 45
-
 News
NewsCOVID-19 pandemic tied to low birth weight for infants in India
The incidence of low birth weight rose sharply in India amid the COVID-19 pandemic, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsResearchers awarded $308k grant to study the role of gut microbiomes to improve outcomes in dystonia
Scientists are undertaking a study that will investigate the role of the gut microbiome in dystonia, a movement disorder of abnormal postures and involuntary twisting or repetitive movements, to improve neurobehavioral outcomes.
-
 News
NewsRecombinHunt: predicting new pandemics through data analysis
A study presents the promising results of RecombinHunt, a new data-driven method which can identify, with high accuracy and computational efficiency, recombinant SARS-CoV-2 genomes with one or two breakpoints.
-
 News
NewsScientists ID novel host factors that facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry
Researchers have identified new host factors that interact with the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to promote viral entry.
-
 News
NewsFunctional predictability of universal gene circuits in diverse microbial hosts
By developing a quantitative framework to explore the universality and reliability of biological parts in non-model organisms, the team characterized universal genetic parts in four microbial hosts that can be used to build biological circuits in living cells.
-
 News
NewsRevealed: new factor associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 in people with obesity
By analyzing samples from obese non-diabetics, researchers found that high blood levels of saturated fatty acids cause pre-activation of innate immune cells that, when infected with SARS-CoV-2, produce elevated levels of inflammatory molecules.
-
 News
NewsTreatment with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides can impede antibiotic resistance
A common infection-causing bacteria was much less likely to evolve antibiotic resistance when treated with a mixture of antimicrobial peptides rather than a single peptide, making these mixtures a viable strategy for new antibiotic treatments.
-
 News
News Bacteria detected in tattoo and permanent makeup inks
Researchers have detected anaerobic and aerobic bacteria in commercial tattoo and permanent makeup inks. The findings demonstrate that the inks could be a source of human infections.
-
 News
NewsUN publishes negotiation proposals for sharing benefits from plant, animal, microbial DNA sequences
New UN documents provide proposals and options to meet a global pledge to share fairly some of the multi-trillion-dollar revenues and other benefits derived from products related to the use of “digital sequence information on genetic resources (DSI)”.
-
 News
NewsMicroscopic fungi enhance soil carbon storage in new landscapes created by shrinking Arctic glaciers
Melting Arctic glaciers are in rapid recession, and microscopic organisms colonise the newly exposed landscapes. A new study reveals that yeasts play an important role in soil formation in the Arctic after glaciers have melted away.
-
 News
NewsResearchers examine how fungal toxins impact hormones in pregnancy
A fungal toxin that hinders animal fertility and fetal development may also disrupt human sex hormones in pregnancy, according to a study.
-
 News
NewsChanging the gut microbiome boosts health outcomes for people newly diagnosed with metastatic kidney cancer
Researchers have developed a novel use of biotherapeutic product CBM588 in the treatment of cancer; new research suggests the agent adjusts people’s microbiome, possibly leading to enhanced effectiveness of FDA-approved cancer immunotherapies.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough research makes cancer-fighting viral agent more effective
Researchers from Aarhus University have made a significant breakthrough by discovering that the drug 4-OI can enhance the effectiveness of a cancer-fighting viral agent. This may lead to treatment of cancers that are otherwise resistant to therapies.
-
 News
NewsBird flu stays stable on milking equipment for at least one hour
Bird flu, or H5N1 virus, in unpasteurized milk is stable on metal and rubber components of commercial milking equipment for at least one hour, increasing its potential to infect people and other animals, report researchers.
-
 News
NewsCoumarin glycosides reverse enterococci-facilitated enteric infections
Researchers have developed a dietary therapeutic for enterococci-mediated infections.
-
 News
NewsCommon respiratory infections may have protected children from COVID-19, study suggests
Analyzing nasal swabs taken during the pandemic, researchers suggest that the frequent presence of other viruses and bacteria may have helped to protect children from the worst effects of COVID-19 by boosting their immune systems.
-
 News
NewsResearchers thwart resistant bacteria’s strategy
Researchers have discovered a weakness in Pseudomonas aeruginosa with the potential to become the target for a new way to attack it.
-
 News
NewsDegradation of cell wall key in the spread of resistance
A new study shows how an enzyme breaks down the bacteria’s protective outer layer, the cell wall, and thus facilitates the transfer of genes for resistance to antibiotics.
-
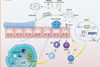 News
NewsResearchers harness intratumoral microbiome against colorectal cancer
Scientists have established a microbiota-targeted drug delivery system that exhibits high efficiency in colorectal cancer targeting and colon retention.
-
 News
NewsLong-standing marine mystery solved: How algae get nitrogen to grow
In a new study, scientists have shed light on an unexpected partnership: a marine diatom and a bacterium that can account for a large share of nitrogen fixation in vast regions of the ocean.

