More News – Page 151
-
 News
NewsDigital test directly measures HIV viral load
Researchers have developed a time and cost-efficient digital assay that can directly measure the presence of HIV in a single drop of blood.
-
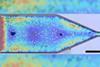 News
NewsResearchers can use ultrasound to control orientation of small particles, including bacteria
Using ultrasound technology and a nozzle, scientists have separated, controlled and ejected different particles based on their shape and various properties, with implications for drug delivery and bioprinting.
-
 News
NewsD-amino acids play role in cholera bacterium’s bid to escape
Cholera bacteria use specific D-amino acids to escape unfavourable niches and form complex ecological systems, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsWarning as third of toddlers found to have unmet vaccination needs
A third of under-fives attending a Paediatric Emergency Department (PED) and who are eligible for pre-school boosters have unmet vaccination need according to new research.
-
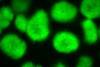 News
NewsStreptomycetes reveal their arsenal of signalling compounds
Streptomyces bacteria produce a group of signalling molecules that trigger a variety of processes, a new study shows.
-
 News
NewsSmall ruminant farms could spread human diarrhoea causing bug
Goat and sheep dairy farms are a potential transmission source for a bacteria that can cause human gastroenteritis, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsStudy unveils gene expression of photosynthetic symbiont in marine diatom
A new study explores the genetic expression of a photosynthetic symbiont that lives inside an abundant marine organism.
-
 News
NewsMonitoring bats can help ID coronaviruses with pathogen potential
Researchers who found novel coronaviruses in UK bats say genetic surveys of the viruses should be regularly conducted, even if none of those viruses can infect humans yet.
-
 News
NewsDUV LEDs offer rapid inactivation of human respiratory RNA viruses
A deep ultraviolet LED based on AlGaN, whose wavelength is tunable from 365 to 210 nm, is a perfect alternative to mercury lamps to inactivate human respiratory RNA viruses due to its pollution-free, small-size and energy-conservation qualities.
-
 News
NewsAutism-specific metabolic pathways linked to gut microbes
A reanalysis of previous studies has identified autism-specific metabolic pathways associated with particular human gut microbes - these were also seen elsewhere in autistic individuals, from their brain-associated gene expression profiles to their diets.
-
 News
NewsResearchers reveal how Leishmania parasite uses immune cells as Trojan Horse
A new study found that the parasite targets a receptor on the surface of the neutrophil to gain access to the cell, and once inside the parasite resists the neutrophils’ pathogen-killing molecules.
-
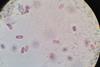 News
NewsRule-breaking anoxic bacteria infected with viruses
Researchers investigating why green and purple bacteria in northeast Washington didn’t obey the usual rules found they had genes in their metagenome that came from viruses.
-
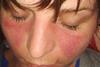 News
NewsLupus flare-ups linked to Ruminococcus blautia gnavus blooms in gut
A new study found that bacterial blooms of the gut bacterium Ruminococcus blautia gnavus occurred at the same time as disease flare-ups in five of 16 women with lupus of diverse racial backgrounds studied over a four-year period.
-
 News
NewsMagnetic bacteria found on deep sea vents
Magnetotactic bacteria that ‘sense’ the Earth’s magnetic field have been found on deep undersea vents.
-
 News
NewsHeart drug peruvoside could prevent spread of up to 12 viruses
Peruvoside, a plant-based compound that is commonly used to treat heart failure, has been discovered to be able to prevent up to 12 medically important viruses, all originating from different virus families.
-
 News
NewsComplex life descended from common Asgardian ancestor
Researchers analyzing the genomes of hundreds of different archaea have discovered that eukaryotes trace their roots to a common Asgard archaean ancestor.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal how Captain Cook microbe forms clumps
Researchers have described for the first time how the marine microorganism Trichodesmium filaments form aggregates through a simple yet exquisitely effective behavioural strategy.
-
 News
NewsGlobal warming accelerates CO2 emissions from soil microbes
Emissions of CO2 by soil microbes into the Earth’s atmosphere are not only expected to increase but also accelerate on a global scale by the end of this century, a new study suggests.
-
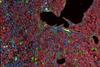 News
NewsEngineered lung cells light up when Covid sparks immune response
Scientists have engineered lab-grown lung epithelial cells to light up red in colour once they launch an immune response, creating a tool that can be used to screen for drugs that can help treat COVID-19 and other emerging infections.
-
 News
NewsHorseradish roots switched out for biolab-made enzyme
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in the production of important enzymes that were previously extracted from horseradish roots, but now can be produced recombinantly in the laboratory.

