More clean water – Page 10
-
 News
NewsFrom Yemen to Mayotte, the spread of a highly drug-resistant cholera strain
Scientists have revealed the spread of a highly drug-resistant cholera strain. The strain is resistant to ten antibiotics – including azithromycin and ciprofloxacin, two of the three recommended for treating cholera – and was identified for the first time in Yemen in 2018-2019.
-
 News
NewsScientists collect ‘microbial fingerprints’ found in household plumbing
Scientists sampled faucets in eight homes for seven days to see the flow and change of different bacteria populations. They found that, though houses generally shared major categories of bacteria, down to the species level, there was wide variation from house to house.
-
 News
NewsFlu virus remains infectious in refrigerated raw milk
Influenza or flu virus can remain infectious in refrigerated raw milk for up to five days, a new study reveals. The findings come at a time when outbreaks of bird flu in dairy cattle have raised concerns about the potential for a new pandemic.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial oxidation in glacial rivers and lakes could help mitigate methane emissions
A new study suggests microbes in glacial rivers and lakes may play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of methane, a powerful greenhouse gas that recent studies have shown emerging as glaciers melt in warming global temperatures.
-
 News
NewsHidden threats to soil revealed in sewage sludge research
Hidden threats from the agricultural use of contaminated sewage sludge could be contributing to already diminished poor soil health, according to a new report.
-
 News
NewsUrgent need for integrated detection strategies for AMR in water environments
A new review calls attention to the urgent need for integrated detection strategies that combine the precision of molecular tools with the cost-effectiveness of traditional methods which could enable more efficient, accessible, and scalable AMR monitoring.
-
 News
NewsResearchers call on the European Commission to protect groundwater and subterranean life from pollution
A plea was published in two days after the European Parliament approved revisions to water quality assessment standards.
-
 News
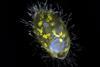
NewsUnusual endosymbionts crop up all over the world
Scientists have discovered peculiar mitochondria-like symbionts all over the world, and unveiled their surprising metabolic capacities in a new study.
-
 News
NewsSatellite evidence bolsters case that climate change caused mass elephant die-off
New analysis showing carcass distribution and algae in watering holes points to climate-induced poisoning of over 300 African elephants.
-
 News
NewsCold plasma isn’t just for sterilisation - it could become a vital green tool in water purification
Cold plasma isn’t just for sterilisation, but offers potential as a sustainable water treatment that can target stubborn contaminants like biofilms and pharmaceuticals, according to a new review.
-
 News
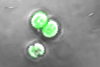
NewsResearchers develop light-guided siRNA delivery system based on cyanobacteria
In a study published in Cell Reports Physical Science on Nov. 25, a research team led by Prof. Cai Lintao from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported its development of an innovative intelligent light-guided biohybrid system, the CTPA/siCSF1R system, to target tumor-associated ...
-
 News
NewsResearchers catalog the microbiome of US rivers
River microbes found near wastewater treatment plants expressed high levels of antibiotic resistance genes, reveals a study of the presence and function of microbes in rivers covering 90% of the watersheds in the continental U.S.
-
 News
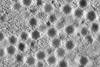
NewsNew edition of book explores ranavirus infection and disease in amphibians, reptiles and fish
Researchers are providing new information and guidance on monitoring and managing viruses that cause life-threatening diseases in amphibians, reptiles and fish, as detailed in a new book edition.
-
 News
NewsFunding boost to bring engineering biology technologies to market
Part of a £2.8 million UKRI seed corn fund has been awarded to the Environmental Biotechnology Innovation Centre (EBIC) to bridge the gap between research and market-ready products and technologies, with comprehensive support and resources for researchers.
-
 News
NewsGreener and cleaner: Yeast-green algae mix improves water treatment
Researchers have discovered that yeast and green algae form the best combination in terms of boosting wastewater treatment efficiency.
-
 News
NewsEpidemiologic features and evidence of new subtypes of Cryptosporidium parvum in diarrheic calves in Egypt
A new study examines the prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp. infections in diarrheic calves reared in different localities in Egypt under different management systems.
-
 News
NewsSewage surveillance proves powerful in combating antimicrobial resistance
A study is using sewage surveillance as a vital strategy in the fight against diseases that spread through the water such as legionella and shigella.
-
 News
NewsMulticellular organisms require significantly more energy than single-celled ones
A new study shows that multicelled organisms like the metazoan daphnia require a tenfold increase in energy compared with protists for their growth, maintenance and survival.
-
 News
NewsStandard methodologies failing to accurately quantify fecal contamination across the globe, study warns
Standard risk assessment methodologies are significantly underestimating fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) loads in contaminated water, including recreational waters used for the 2024 Olympics, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsPathogens that cling to microplastics may survive wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment fails to kill several human pathogens when they hide out on microplastics in the water, reports a new study.
