All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 88
-
 News
NewsScientists repurpose gene editing tool to help uncover hidden microbial diversity
Pioneering research has repurposed a gene editing tool to help shed light on the true biodiversity present in natural environments. The study could help pave the way for more productive soils and improved health.
-
 News
NewsAtomic imaging and AI offer new insights into motion of parasite behind sleeping sickness
Researchers applied leading-edge atomic imaging and AI-driven modeling to create the most detailed 3D map yet of the flagellum on Trypanosoma brucei, which causes sleeping sickness.
-
 News
NewsControlling starch levels in algae could have biotechnology and sustainability benefits
Researchers have found a new method to control starch storage in algae - a finding with potential applications in areas such reducing greenhouse gases. Modifying a blue light-activated signalling pathway makes it possible to regulate storage, they say.
-
 News
NewsNo more copy-pasting: DNA base editing for better Lactobacillus strains
Scientists were able to edit the DNA of Lactobacillus strains directly without a template from other organisms. This technique is indistinguishable from natural variation and enabled them to create a strain that doesn’t produce diabetes-aggravating chemicals.
-
 News
NewsOpen benchmarking of CycloneSeq™ for complete bacterial genomes
Benchmark data and analysis of new CycloneSEQ using novel nanopore sequencing technology demonstrates the ability to sequence complete bacterial genomes.
-
 News
NewsTransatlantic collaboration to develop therapeutic for Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever
A new transatlantic collaboration will look to develop an affordable and accessible monoclonal antibody therapeutic for Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (CCHFV), which could treat and protect thousands of people globally.
-
 News
NewsInfectious disease surveillance platform BEACON launches as a new open-source global resource
The Biothreats Emergence, Analysis and Communications Network (BEACON), an open-source infectious diseases monitoring tool powered by AI and human experts, has been launched.
-
 News
NewsPsilocibin or ‘magic mushroom’ use in US increased among all age groups since decriminalization in 2019
The prevalence of psilocybin use in the US has increased across all age groups between 2014 and 2023, with those with mental or physical comorbidities among the most common users.
-
 News
NewsSugar-mimicking molecule central to virulence of a common crop disease, study finds
A strain of Pseudomonas syringae manipulates plants by producing a substance called glycosyrin to suppress the immune response. New research shows that glycosyrin does this by mimicking galactose, acting like a wolf in sheep’s clothing.
-
 News
NewsStudy: Experimental bird flu vaccine excels in animal models
A vaccine has demonstrated complete protection in mice against a deadly variant of the virus that causes bird flu. It focuses on the H5N1 variant known as 2.3.4.4b, which has caused widespread outbreaks in wild birds and poultry.
-
 News
NewsNew giant virus isolated in Jyväskylä for the first time in Finland
For the first time in Finland, researchers have isolated a giant virus, which was named Jyvaskylavirus. The discovery shows that giant viruses are more common in northern regions than researchers have thought.
-
 News
NewsStrongest hints yet of biological activity outside the solar system
Astronomers have detected the chemical fingerprints of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) and/or dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), in the atmosphere of the exoplanet K2-18b. On Earth, these are only produced by life, primarily microbial life such as marine phytoplankton.
-
 News
NewsMicroorganisms employ a secret weapon during metabolism
Microorganisms have evolved a variety of methods for fixing carbon. Researchers investigated the methods that are utilized at extremely hot, acidic and sulfur-rich hydrothermal vents in shallow waters off the island of Kueishantao, Taiwan.
-
 News
NewsFrequent use of antibiotics in infants and young children may increase risk for asthma, allergies and other conditions
Researchers have found that repeated antibiotic use before age 2 is associated with a higher risk for asthma, food allergies and hay fever later in life. These findings also applied to siblings who had different experiences with antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotic-resistant Escherichia albertii on the rise in Bangladeshi chicken shops
Researchers have detected alarming rates of Escherichia albertii in retail chicken meat in Bangladesh. Their findings show extensive contamination and significant antimicrobial resistance, underscoring the potential risks to public health.
-
 News
NewsThe very first structural images of a tuberculosis-fighting virus
Scientists have used advanced imaging techniques to provide a detailed look at how a tiny virus, known as a phage, invades Mycobacteria. The research could pave the way toward phage-based treatments for antibiotic-resistant mycobacteria.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop innovative solution for tracking antibiotic resistance genes
Scientists have developed a computational tool, Argo, designed to accurately track ARGs in environmental samples, providing insights into their dissemination and associated risks.
-
 News
NewsDr. Sabine Ehrt named Chair of the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine
Dr. Sabine Ehrt, an internationally renowned leader in tuberculosis research, has been appointed chair of the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
-
 News
NewsLiving fungus-based building material repairs itself for over a month
Engineers have developed a building material that uses the root-like mycelium of a fungus and bacteria cells. They show that it is capable of self-repairing and could eventually offer a sustainable alternative for high-emission building materials like concrete.
-
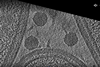 News
NewsResearchers release phage images with unprecedented detail
Researchers have produced the most detailed image to date of a bacteriophage, that has allowed them to see for the first time the structural makeup of the part of the phage that directly attaches to its target Mycobacterium cell.
