All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 58
-
 News
NewsSurvey finds epidemiologists believe viral and mosquito-borne pathogens are priority concerns for disease outbreaks
A new survey reveals that infectious disease experts point to viral pathogens and mosquito-borne pathogens as likely to spark outbreaks as humans, animals and viruses overlap; and new viruses are as concerning as changes to existing viruses.
-
 News
News‘Food theft’ among seabirds could be transmission point for deadly avian flu
The deadly H5N1 avian influenza virus, which has killed millions of birds worldwide since 2021 – and in rare cases can be transmitted to humans – may be spread through the food-stealing behaviour of some seabirds.
-
 News
NewsUS COVID-19 rates show oscillating waves every six months
COVID-19 cases in the U.S. have shown unexpected oscillating waves every six months between the southern states and the northern states and, to a lesser degree, from east to west, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsResearchers take power and efficiency of biological sensing to record level
Scientists have developed a new biological sensing method that can detect substances at the zeptomolar level – an astonishingly miniscule amount.
-
 News
NewsX.J. Meng receives prestigious MERIT Award to study hepatitis E virus
The Meng Lab will receive about $2 million over the next five years with the opportunity to seek approval to renew without undergoing regular peer review for five more years for up to $2.4 million, as the lab continues its cutting-edge research on hepatitis E virus.
-
 News
NewsFred Hutch launches Atlas of Inspiring Hispanic/Latinx Scientists
To highlight and celebrate the many contributions of Hispanic and Latinx scientists, Fred Hutch Cancer Center has launched an Atlas of Inspiring Hispanic/ Latinx Scientists.
-
 News
NewsMonoclonal antibodies offer hope for tackling antimicrobial resistance
Monoclonal antibodies – treatments developed by cloning a cell that makes an antibody – could help provide an answer to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance, say scientists.
-
 News
NewsWyss Institute selected to develop biologically engineered broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapeutic
The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University received a contract for up to $12M from the new SHIELD program which aims to develop a prophylactic treatment that can rapidly clear multiple bloodborne bacterial and fungal pathogens.
-
 News
NewsCofitness network connectivity determines a fuzzy essential zone in open bacterial pangenome
Based on a robust Tn-seq analysis of independent mariner transposon insertion libraries of Sinorhizobium strains, scientists have identified a strain-dependent variation in the fitness network of the Sinorhizobium pangenome under a nutrient-rich condition.
-
 News
NewsMore than 39 million deaths from AMR infections estimated between now and 2050
More than 39 million people around the world could die from antibiotic-resistant infections over the next 25 years, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsCRISPR/Cas9 modifies euglena to create potential biofuel source
Using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit the genome of Euglena gracilis, researchers have produced stable mutants that created wax esters two carbons shorter than the wild-type species. This makes them more applicable as feedstock for biofuels.
-
 News
NewsPlant prebiotics offer new ally in the fight against pathogens
Disruptions to the community of microbes that live inside the leaves of a spindly plant called <i>Arabidopsis</i> can compromise a plant’s ability to tell harmless invaders from harmful ones – effectively turning the plant’s defensive arsenal against itself.
-
 News
NewsRamie rhizosphere study unveils secrets of the volcano
Volcanic soil plays a key role in the formation of microbial community diversity and subsequently influences the diversity of microorganisms residing in the rhizosphere of Boehmeria nivea L.
-
 News
NewsSoil pH is driver of microbial community composition - and need to address toxicity shapes the community
Researchers have determined through both statistical analysis and in experiments that soil pH is a driver of microbial community composition – but the need to address toxicity released during nitrogen cycling ultimately shapes the final microbial community.
-
 News
NewsMicrobe dietary preferences influence the effectiveness of carbon sequestration in the deep ocean
The movement of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the surface of the ocean to the deep ocean depends on a number of seemingly small processes - including the dietary preferences of bacteria that feed on organic molecules called lipids.
-
 News
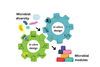
NewsComputer-aided biology can be deployed to develop tailored microbe communities
Researchers inspired by natural lichens want to develop the microbial networking manifested here as an example for future applications, as a contribution toward establishing interdisciplinary methods and technologies for CO2-negative processes.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop promising Lassa fever vaccine
Researchers have developed a promising new vaccine candidate that protects against Lassa fever. The vaccine effectively prevents severe cases of the disease and death in preclinical animal models and paves the way for research in people.
-
 News
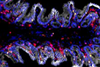
NewsGut microbiome influences location and type of immune cells
Researchers have found that different anatomical sections of the gastrointestinal tracts of mice carry different compositions of microbial communities, and the specific makeup of the microbiota can influence the type and abundance of immune cells in any particular region.
-
 News
NewsSome guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis E virus infection need a revamp, evaluation finds
A systematic evaluation of HEV infection guidelines revealed significant variability in their quality and recommendations. While some demonstrated strengths, others were found lacking in stakeholder involvement, rigor of development, and applicability.
-
 News
NewsCatalogue of fungi in China reveals new taxa of macrofungi from southern Xizang
During a field trip in July 2023 in the Himalayas, 882 specimens in six counties from the border area of Xizang, China were collected, among which 15 new macrofungal species were revealed and are described in the study.
