All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 31
-
 News
NewsNew vaccine shows promise against typhoid and invasive salmonella in first human trial
Researchers have completed a successful Phase 1 clinical trial of a novel vaccine designed to protect against both typhoid fever and invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella–two major causes of illness and death among children in sub-Saharan Africa.
-
 News
NewsProfessor awarded $3.9 million to fight deadly parasites that threaten children and immunocompromised adults
A multi-institutional team will develop effective drugs that are urgently needed to manage cryptosporidiosis in young children, immunocompromised adults and as a countermeasure to epidemic outbreaks.
-
 News
NewsCould slime mold microbes be a source of potent antimicrobials?
The cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum is a soil microbe that produces diverse natural products with potential antibiotic activity. In this study, researchers optimized lab culture conditions of Dictyostelium cells to boost the levels of low-abundance chlorinated compounds and to characterize their antimicrobial properties.
-
 News
NewsDo imported cut flowers spread livestock viruses?
A study investigated whether Culicoides biting midges are being accidentally exported from Africa to Europe in shipments of cut flowers. Although researchers did detect small numbers of these insects near and inside greenhouses on a Kenyan flower farm, they found none in packaging or transport areas.
-
 News
NewsTrailblazing Young Scientists honored with $250,000 prizes at Blavatnik National Awards Gala
Three of America’s most promising young scientists were awarded top honors at the 2025 Blavatnik National Awards for Young Scientists, one of the country’s most significant prizes for early-career researchers. The Life Sciences Laureate was Philip J. Kranzusch, Harvard Medical School (Microbiology).
-
 News
NewsNew study reveals where HIV hides in different parts of the body
A new study reveals that HIV cloaks itself in the DNA of infected cells using unique DNA patterns in the brain, blood and parts of the digestive tract. For example, in the brain, the virus avoids genes and hides in less active parts of the DNA.
-
 News
NewsYeast proteins reveal the secrets of drought resistance
A new study in Cell Systems helps explain how organisms can come back from desiccation (the removal of water or moisture) while others fail by looking at the cell’s proteins. In the first survey of its kind, a team of researchers profiled thousands of proteins at once for their ability to survive dehydration and rehydration.
-
 News
NewsScientists blaze new path to fighting viral diseases
Scientists have identified a potential new drug against the virus that causes COVID-19 - and devised a powerful new platform for finding medicines to fight many types of infectious diseases. Compound 6, led SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins to misfold, malfunction, and ultimately, be destroyed and removed by cells, in lab tests.
-
 News
NewsBiodegradable microplastics rewire carbon storage in farm fields
A pioneering two-year field study has revealed that biodegradable microplastics, often hailed as eco-friendly alternatives to conventional plastics, are quietly reshaping the chemistry of farmland soils in unexpected and complex ways. They attracted a special group of microbes known as K-strategists—slow-growing, efficient decomposers.
-
 News
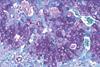
News‘Good’ gut bacteria boost placenta for healthier pregnancy
Research has found the first clear evidence that the ‘good’ gut bacteria Bifidobacterium breve in pregnant mothers regulates the placenta’s production of hormones critical for a healthy pregnancy. Pregnant mice without Bifidobacterium breve in their gut had a higher rate of complications, and increased fetal loss.
-
 News
NewsMicroplastics found to change gut microbiome in first human-sample study
New research presented today at UEG Week 2025 shows that microplastics can alter the human gut microbiome, with some changes resembling patterns linked to depression and colorectal cancer.
-
 News
NewsGolden spruce trees: Gold forms nanoparticles in the needles – bacteria show the way
A new study has, for the first time, uncovered a connection between bacteria living in Norway spruce needles and gold nanoparticles. This discovery could pave the way for environmentally friendly gold exploration methods, while examining similar processes in mosses may also help remove metals from mining-impacted waters.
-
 News
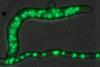
NewsIncrease in cell volume and nuclear number of the Koji fungus enhances enzyme production capacity
This study revealed cellular traits of the koji fungus Aspergillus oryzae linked to enzyme production through cell biological analysis. The authors found that, over time in culture, hyphae thicken, resulting in a tenfold increase in cell volume. Simultaneously, the number of nuclei per hyphal cell also rises tenfold, exceeding 200.
-
 News
NewsExperimental mapping of bacterial growth reveals evolutionary and ecological patterns
A research team has proposed a new approach to reveal ecological niches (positions within ecosystems) and evolutionary relationships in nature through large-scale growth analysis of bacteria in strictly regulated laboratory settings.
-
 News
NewsFinal Call: Submit your breakthrough for the 2025 ISM × RIKEN Microbiota Innovation Awards in Tokyo
Yakult, Meiji, Morinaga, Metagen and other industry pioneers join global scientists at Happo-en to celebrate microbiota-driven discoveries; nominations close October 7, 2025
-
 News
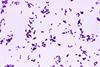
NewsMap of bacterial gene interactions reveals potential drug targets
Researchers have developed a new technique called Dual transposon sequencing (Dual Tn-seq), which allows for rapid identification of genetic interactions. It maps how bacterial genes work together, revealing vulnerabilities that could be targeted by future antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsAntibody discovered that blocks almost all known HIV variants in neutralization assays
An international research team has discovered an antibody that could advance the fight against HIV. The newly identified antibody 04_A06 proved to be particularly effective in laboratory tests. It was able to neutralize 98.5 percent of more than 300 different HIV strains, making it one of the broadest antibodies against HIV identified.
-
 News
NewsRocket test proves bacteria survive space launch and re-entry unharmed
A world-first study has proven microbes essential for human health can survive the extreme forces of space launch. The study found the spores of Bacilus subtilis, a bacterium essential for human health, can survive rapid acceleration, short-duration microgravity and rapid deceleration.
-
 News
NewsResearchers wake up microbes trapped in permafrost for thousands of years
In a new study, a team of geologists and biologists resurrected ancient microbes that had been trapped in ice—in some cases for around 40,000 years.
-
 News
NewsMarine heatwaves have hidden impacts on ocean food webs and carbon cycling
A new study analyzing data from robotic floats and plankton records reveals how marine heatwaves reshape ocean food webs and slow transport of carbon to the deep sea.
