All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 187
-
 News
NewsNew Staph spa type emerges in Jordan as primary cause of dairy bovine mastitis
A new spa type of Staphylococcus aureus has emerged in Jordan which has been identified as the primary cause of dairy cow mastitis in the region.
-
 News
NewsImmune systems develop ‘silver bullet’ defences against common bacteria
Immune systems develop specific genes to combat common bacteria such as those found in food, new research shows.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough harnesses mRNA technology to develop malaria vaccine
A new mRNA vaccine targeting immune cells in the liver could be the key to tackling malaria, a disease that causes over half a million deaths each year, yet has no effective long-lasting vaccine.
-
 News
NewsMolecular biologists identify framework for understanding RNA editing in a disease-causing parasite
Researchers have determined the architecture of the molecular machines that harbour gRNA strands and allow those strands to engage mRNA in the single-celled, disease-causing parasite Trypanosoma brucei.
-
 News
NewsResearchers use mass spectrometry to explore antimicrobial resistance
Researchers are using single-cell mass spectrometry to determine whether cells with persistent pathogens will also have less intracellular drug levels to potentially explain antimicrobial treatment failure.
-
 News
NewsNew treatment paves way to tackle chicken infections resistant to antibiotics
An innovative treatment paves the way for reducing antimicrobial resistance in the treatment of a deadly infection in chickens, according to an international team of researchers led by the University of Surrey.
-
 News
NewsResearchers uncover novel bacterial communication system to combat AMR
Using a sophisticated mass spectrometry technology developed at SMART and MIT, researchers have discovered that the enzyme RlmN is a stress sensor for reactive oxygen species (ROS) – highly reactive molecules which can cause damage to bacteria. Source: SMART AMR (L to R) SMART researchers Dr Cui Liang, ...
-
 News
NewsBioengineered yeast devouring agricultural waste could close carbon circle
Researchers report making modified yeast that can feed on a wider range of materials, many of which can be derived from agricultural by-products that we don’t use known as waste biomass.
-
 News
NewsClose contact within households may not influence COVID-19 transmission
A study measuring the impact of close contact on SARS-CoV-2 virus transmission within households suggests that being in proximity to someone with the virus may not influence the likelihood of becoming infected.
-
 News
NewsMulticellular life on Earth ‘didn’t arise as described in textbooks’
Oxygen didn’t catalyze the swift blossoming of Earth’s first multicellular organisms, a new study says, defying a 70-year-old assumption about what caused an explosion of oceanic fauna hundreds of millions of years ago.
-
 News
NewsPicolinic acid reveals its broad-spectrum antiviral abilities
Picolinic acid, a natural compound produced by mammalian cells, can block several disease-causing viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A viruses, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsMicrobiologist and virologist creating Global Pandemic Research Alliance
Columbia University virologist Professor David Ho and The University of Hong Kong (HKU) microbiologist Professor Kwok-yung Yuen are teaming up to create a global alliance for conducting research in emerging infectious diseases.
-
 News
NewsNew MenB vaccine heralds use of genetic vaccines to combat bacterial diseases
A vaccine candidate that can protect children from Meningococcal group B (MenB), which can lead to meningitis, has progressed to clinical development, researchers say.
-
 News
NewsScientists track global atmospheric spread of harmful microbes
Researchers have published an article that helps to understand the intercontinental spread of harmful microorganisms through the atmosphere.
-
 News
NewsPartnership to use AI to speed up vaccine development against Disease X
CEPI, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, and the Houston Methodist Research Institute (HMRI), have announced a partnership to combine cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) technology with established laboratory techniques to speed up development of future vaccines against novel viral threats.
-
 News
NewsGlobal overview of antibiotic resistance determinants yields surprising findings
Scientists have developed a statistical model of the main determinants behind worldwide antibiotic resistance dynamics based on a large-scale spatial-temporal analysis.
-
 News
NewsStudy suggests the carbon cycle is speeding up
In Northern ecosystems, rising temperatures are depleting the soil carbon reservoir, a new study reveals.
-
 News
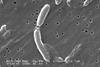
NewsNew cholera substrains in Bangladesh uncovered by genomic surveillance
Researchers have uncovered two new cholera substrains in a displaced refugee population in southern Bangladesh, where a pre-emptive mass vaccination campaign of over one million refugees was successful in preventing an epidemic.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover novel biomarker for sepsis severity
Scientists have identified a novel biomarker that could change the way sepsis is approached and treated.
-
 News
NewsScorpionfish protein kills drug-resistant bacteria from patients with cystic fibrosis
A scorpionfish protein effectively kills antibiotic-resistant bacteria from patients with cystic fibrosis, escaping an immune response that renders the human version of the protein ineffective.
