All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 134
-
 News
NewsMaternal antibodies interfere with malaria vaccine responses
Maternal antibodies passed across the placenta can interfere with the response to the malaria vaccine, which would explain its lower efficacy in infants under five months of age, according to research.
-
 News
NewsNew tool enables a more complete and rapid decoding of the language of algal gene expression
A new method that research teams can use to measure and compare different forms of proteins and protein complexes helped reveal a previously unseen molecular signature of how algal genomes are controlled during the cell cycle.
-
 News
NewsRepeated COVID vaccines enhance mucosal immunity against the virus
New work has found that repeated Covid-19 vaccinations lead to the presence of mucosal antibodies, for example, inside the nose.
-
 News
NewsMeet the Global Ambassadors: Our Q&A with Matthew B Sullivan
The Microbiologist chats with our new Global Ambassador for the United States, Matthew B Sullivan, who is Professor of Microbiology and Director of the Center of Microbiome Science, at The Ohio State University.
-
 News
NewsPolar bears’ exposure to pathogens is increasing as their environment changes
As the Arctic warms, polar bears now face a greater risk of contracting several pathogens than bears three decades ago, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsNovel antibody platform tackles viral mutations
Scientists have developed an innovative antibody platform aimed at tackling one of the greatest challenges in treating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2: their ability to mutate and evade existing vaccines and therapies.
-
 News
NewsFull-bodied cheese flavor–prediction of flavor development soon possible thanks to new method
Peptides formed during cheese ripening are crucial for the full-bodied flavor of aged cheeses, known as kokumi. Researchers have now developed a new method to analyze these flavor-relevant peptides precisely, quickly, and efficiently.
-
 News
NewsTire-wear particles disrupt gut-liver function in aquatic organisms
Researchers have uncovered the adverse health effects of tire-wear particles (TWPs) on aquatic organisms. The study focused on the hepatotoxicity of TWP leachates, revealing significant impacts on the gut-liver axis and oxidative stress levels in test organisms.
-
 News
NewsResearchers probe parasite transmission in turkey flocks
As scientists learn more about a deadly parasite’s ability to move from host to host in turkey flocks, a long-standing theory is in question and opens the door to new preventative measures. Source: U of A System Division of Agriculture photo Histomonosis is a deadly disease to turkeys. ...
-
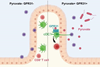 News
NewsStudy reveals how our gut cells detect harmful invaders
Researchers hve found that the GPR31 path in ‘gut surveillance’ cells detects bacterial metabolites and triggers immune responses, opening new possibilities for drug development, vaccines, and probiotics to fight infections.
-
 News
NewsFloor swabbing could help prevent COVID-19 outbreaks in hospitals
In two Ontario hospitals, high levels of SARS-CoV-2 on floors correlated with COVID-19 cases among healthcare workers and patients, suggesting floor swabbing as a potential method to prevent outbreaks.
-
 News
NewsPlastic mulch is contaminating agricultural fields
Using plastic sheets for weed control, even under current best management practices, pollutes soil with macro- and micro-plastics and negatively affect critical soil functions, according to a study.
-
 News
NewsMajor antimicrobial power boost as phages form into surprising flower shapes
Researchers treated bacteria-eating viruses so they could be viewed alive under an electron microscope and coaxed them to join together into flower-like shapes - discovering that this made them 100 times more efficient.
-
 News
NewsMicrobes drove methane growth between 2020 and 2022, not fossil fuels, study shows
Microbes in the environment, not fossil fuels, have been driving the recent surge in methane emissions globally, according to a new, detailed analysis.
-
 News
NewsStudy uncovers how Covid-19 is so good at defeating the innate immune response
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has an enzyme that can counteract a cell’s innate defense mechanism against viruses, explaining why it is more infectious than the previous SARS and MERS-causing viruses.
-
 News
NewsResearchers to deploy fungus to combat devilishly invasive tree-of-heaven
Researchers are examining if a natural fungus that kills the highly invasive tree-of-heaven could be spread to other trees-of-heaven by the spotted lanternfly, in turn reducing populations of this pest insect as well.
-
 News
NewsNew bacterial toxins discovered: A key to fighting infections
Researchers have discovered a new group of bacterial toxins that can kill harmful bacteria and fungi, opening the door to potential new treatments. Found in over 100,000 microbial genomes, they can destroy the cells of bacteria and fungi without harming other organisms.
-
 News
NewsAncient viral DNA in human genome linked to multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
New research has revealed a connection between ancient viral DNA embedded in the human genome and the genetic risk for two major diseases that affect the central nervous system.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals insights into oral HPV incidence and risks in men across 3 countries
A new study has unveiled crucial information about the incidence and risk factors of oral human papillomavirus (HPV) infections among men in the United States, Mexico and Brazil - the virus is linked to up to 90% of all oropharyngeal cancer cases in men in the U.S.
-
 News
NewsChemical trick activates antibiotic directly at the pathogen
Scientists have seen promising results after experimenting with a click-to-release approach that deploys a masked form of colistin to the site of an infection so that it is no longer as damaging to the kidneys while maintaining its high antibiotic efficacy.
