All articles by Linda Stewart – Page 11
-
 News
NewsStudy compares indoor transmission-risk metrics for infectious diseases
A recent study delves into the complex world of assessing the transmission risk of infectious diseases in indoor spaces. Understanding how to accurately evaluate the effectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) has become crucial.
-
 News
NewsReactive nitrogen species dominance is key in the fight against antimicrobial resistance
The balance between two types of molecules – reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) – plays a crucial role in tackling drug-resistant bacteria, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsInterventions could eliminate transmission of hepatitis B from mothers to babies in Africa
Researchers at the University of Liverpool have conducted a large-scale analysis that sheds light on the critical steps needed to combat the vertical transmission of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) in Africa. Source: Solasly A baby in the womb of its mother being held by its mother and ...
-
 News
NewsFlu vaccine offers moderate protection against strains dominant in most European countries in 2024/2025
According to interim analysis of influenza vaccine effectiveness for the 2024/2025 season in Europe, the vaccine offered moderate protection against dominant influenza A strains, and strong protection against influenza B.
-
 News
NewsExperts recommend mAb protection against RSV as standard care for all infants
While RSV poses a serious threat to the health of infants and young children, prophylactic mAbs offer safe and effective protection for an entire season, according to international health organizations.
-
 News
NewsNewly launched Enodia Therapeutics is a biotech company with a new approach for targeted protein degradation
Argobio and the Institut Pasteur have announced the launch of Enodia Therapeutics, a groundbreaking French biotech company dedicated to block and degrade disease-causing proteins for treating cancer, inflammatory diseases and viral infections.
-
 News
NewsTwo different sequence types of Listeria monocytogenes strains used for veterinary vaccines in Russia
Live whole-cell vaccine AUF (LWCV AUF) is used for the prevention of listeriosis in farm animals in Russian regions. A new study investigated whether the two strains used might belong to the same phylogenetic lineage and possess identical sequence types (STs).
-
 News
NewsDiscovery of a common ‘weapon’ used by disease-causing fungi could help engineer more resilient food crops
The discovery of a powerful “weapon” used by many disease-causing fungi to infect and destroy major food crop staples, such as rice and corn, could offer new strategies to bolster global food security
-
 News
NewsDemocratic Republic of the Congo deepens investigation on cluster of illness and community deaths in Equateur province
Health authorities in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and experts from World Health Organization (WHO) are carrying out further investigations to determine the cause of another cluster of illness and community deaths in Equateur province.
-
 News
NewsThe International Space Station is overly sterile - so making it ‘dirtier’ could improve astronaut health
The International Space Station (ISS) has a much lower diversity of microbes compared to human-built environments on Earth, and the microbes that are present are mostly species carried by humans onto the ISS, suggesting that the presence of more microbes from nature could help improve human health in the space station.
-
 News
NewsHidden fungal allies strengthen defenses of black poplars and influence insect interactions
Endophytic fungi inside the leaves strengthen the chemical defenses of black poplars and influence the interactions between insect populations living on the trees.
-
 News
NewsGenomic tools provide clearer view of health for endangered bats
Researchers have used advanced molecular tools to survey the health status of endangered Indiana bats, identifying microbiome changes resulting from parasitic infections.
-
 News
NewsNew method developed to dramatically enhance bioelectronic sensors
In a breakthrough that could transform bioelectronic sensing, researchers have developed a new method to dramatically enhance the sensitivity of enzymatic and microbial fuel cells using organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs).
-
 News
NewsImmunity against seasonal H1N1 flu reduces bird flu severity in ferrets, study suggests
Pre-existing immunity against seasonal H1N1 flu might help explain why most reported human cases of H5N1 bird flu in the U.S. have not resulted in lethal outcomes, suggests a new study.
-
 News
NewsResearch reveals hidden risks from plastic-coated fertilizers in soil
A study focuses on the microplastic pollution generated by polymer-coated, control-release fertilizers, highlighting the need for biodegradable alternatives.
-
 News
NewsA rapid and reproducible method for generating germ-free Drosophila melanogaster
Scientists have introduced a refined method for the production of germ-free Drosophila, complemented by a straightforward verification process to ascertain its efficacy.
-
 News
NewsA*STAR spin-off NalaGenetics implements nationwide drug reaction screening for leprosy patients in Indonesia
NalaGenetics, a spin-off from A*STAR Genome Institute of Singapore (A*STAR GIS), will be transforming leprosy treatments in Indonesia with a nationwide genetic screening programme with their PGx1301 diagnostic kit.
-
 News
NewsMicrobiologist calls for urgent action on the danger of raw sewage in UK seas
A microbiologist has described how he contracted a type of bacterial pneumonia following a swim in the sea that was likely connected to an incident of sewage dumping in the area.
-
 News
NewsScientists build robot to track plant-fungal trade networks, revealing nature’s underground supply chains
New research uses advanced robotics to track the hyper-efficient supply chains formed between plants and mycorrhizal fungi as they trade carbon and nutrients across the complex, living networks that help regulate the Earth’s atmosphere and ecosystems.
-
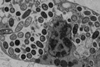 News
NewsBacteria consumed by immune cells become part of the cell
Immune cells that eat bacteria in the body don’t stash them in specialized compartments as once thought, but turn them into critical nutrients that build proteins, create energy and keep the cells alive, according to a new study.
