All Infection Prevention & Control articles – Page 3
-
 News
NewsNature’s 10: Ten people who shaped science in 2025
Microbiologists and scientists tackling infectious diseases are among Nature’s annual list of ten people at the heart of some of the biggest science stories of 2025.
-
 News
NewsPlant phenolic acids supercharge old antibiotics against multidrug resistant E. coli
Plant derived phenolic acids can dramatically enhance the activity of existing antibiotics against multidrug resistant E. coli, offering a promising new tool in the global fight against antimicrobial resistance.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows robust immune responses to H5N8 avian influenza vaccine
A new study shows that the MF59-adjuvanted A(H5N8) vaccine induced strong immune responses, including both functional antibodies and memory T-cell responses, against the vaccine virus, as well as against H5 viruses that have caused recent outbreaks in Europe and the United States.
-
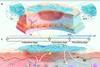 News
NewsMicroenvironment-feedback hydrogel enables precise staged repair of infected wounds
A research team has developed a hydrogel that can sense changes in wound pH and automatically switches its therapeutic behavior from fighting infection to promoting tissue repair.
-
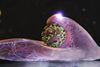 News
NewsResearchers watch live as influenza viruses enter human cells
Using a microscopy technique that they developed themselves, scientists can zoom in on the surface of human cells in a Petri dish, observing live and in high resolution how influenza viruses enter a living cell. They found the cells are not passive, but actively attempt to capture the virus.
-
 News
NewsChemical structures of surface polysaccharides from Acinetobacter baumannii for glycoconjugate vaccines
Researchers provided a comprehensive analysis of the molecules that make up the protective layer of complex sugars on the surface of Acinetobacter baumannii - known as capsular polysaccharides (CPS) and lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and essential for the bacterium’s virulence.
-
 News
News$1.9m grant supports research on chronic wounds
Assistant Professor Carolyn Ibberson at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, has received a four-year, $1.9 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to support research on infections in chronic wounds.
-
 News
NewsResearchers identify bacterial enzyme that can cause fatal heart conditions with pneumonia infections
Researchers have identified a bacterial enzyme that may be the reason some people get heart complications with pneumonia, while others do not. Since enzymes create chemical reactions to help bacteria survive, grow, and sometimes attack tissues, zmpB could become a target for future therapies.
-
 News
NewsTo treat long COVID, we must learn from historical chronic illnesses, medical researchers say
Scientists and doctors have highlighted the importance of studying long COVID in the context of other post-acute infection syndromes or chronic illnesses. By analyzing historical accounts of other epidemics, researchers can gain important perspective on the effects of these chronic illnesses.
-
 News
NewsNew tools saved a million lives from malaria last year but progress under threat as drug resistance rises
Wider use of new tools against malaria, including dual-ingredient nets and WHO-recommended vaccines helped to prevent an estimated 170 million cases and 1 million deaths in 2024, according to WHO’s annual World Malaria Report.
-
 News
NewsResearchers use ‘brain-on-a-chip’ to revolutionize fight against deadly encephalitis viruses
A transparent chip no larger than a stick of gum is helping scientists transform the way researchers study the human brain and develop treatments for some of the world’s deadliest viruses.
-
 News
NewsNew test distinguishes vaccine-induced false positives from active HIV infection
A new device correctly identified those with active HIV-1 infection 95% of the time and those without active infection but with vaccine-induced molecules that could trigger a false positive, 98% of the time.
-
 News
NewsStudy shows common childhood virus can drive bladder cancer development
Tackling a common childhood virus could open the door to preventing bladder cancer, according to new research. The study suggests that a virus most people pick up in childhood can trigger the type of DNA damage that can lead to bladder cancer later in life.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotics could trigger immune response through gut microbiome metabolites
Researchers report how one of the most abundant gut bacteria responds to tetracyclines, a class of commonly prescribed antibiotics. Newly characterized signals released by the bacterium could aid the host’s immune response, inhibit pathogens and restructure the gut microbiome.
-
 News
NewsStudy links childhood vaccination to lower risk of drug-resistant bacteria
Children in Guatemala who received a common vaccine that helps prevent pneumonia were less likely to carry antibiotic-resistant bacteria, according to a new study examining whether rotavirus (RV) and pneumococcal (PCV13) vaccines reduce gut colonization by a group of bacteria.
-
 News
NewsCommon water pill may help HIV medicines work faster and reduce inflammation, early study suggests
Adding a readily available diuretic to standard HIV therapy appears to reduce circulating virus by four-fold, a new study shows. Researchers treated HIV-infected mice with human immune cells with first‑line antiretroviral therapy plus a long‑acting form of spironolactone.
-
 News
News‘Creeping catastrophe’: Climate change is driving global rise in infectious diseases, leading health experts warn
Infectious diseases such as malaria, dengue, and tuberculosis are considered to pose as great a challenge to global health as new or emerging pathogens, according to a study. Participants reported that climate change, poverty, and drug resistance are combining to create an escalating health crisis.
-
 News
NewsPresurgical vaccine may prevent orthopedic device infections
Researchers have developed a novel presurgical vaccine strategy that may prevent dangerous infections in patients receiving hip, knee, and other joint replacements, creating an injectable scaffold designed to stimulate the immune system.
-
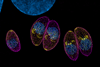 News
NewsToxoplasmosis: How a deadly parasite infects its host cells
Researchers have discovered how the parasite Toxoplasma gondii builds a specialised structure that allows it to move and invade host cells. They identified two proteins that control how the conoid complex is assembled - this acts like an engine for movement and cell-invasion.
-
 News
NewsPositive signs in the fight against superbugs: CHINET 2024 surveillance report
The 2024 CHINET antimicrobial resistance surveillance report uncovers a hopeful trend in China’s battle against bacterial resistance, with a significant reduction in resistance among several key pathogens.
