All Editorial articles – Page 58
-
 News
NewsResearchers uncover new link between gut bacteria and Alzheimer’s disease
A groundbreaking study has revealed a potential link between an infection caused by gut bacteria and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
-
 News
News‘Low risk’ antibiotic has led to an almost untreatable superbug
A new study has found that an antibiotic for liver disease patients could expose them to greater risk of a dangerous superbug.
-
 News
NewsA lung pathogen’s dilemma: infect or resist antibiotics?
Research has uncovered how Pseudomonas aeruginosa manages the trade-off between colonizing and surviving during infection by switching between biofilm formation for antibiotic protection and a more mobile, “planktonic” state to spread and access nutrients.
-
 News
NewsGut bacteria transfer genes to disable weapons of their competitors
New research shows how common gut bacteria tame their antagonistic neighbors by transferring genes that change their weapon systems.
-
 News
NewsBacteria and fungi found on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
Bacteria and fungi from the wings of bats could play a significant role in saving them from white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fungal disease affecting the skin of wings and muzzle, which has nearly wiped out vulnerable bat populations across North America.
-
 News
NewsA metabolic secret of ethane-consuming archaea unraveled
Scientists have presented a study on the degradation of ethane, the second most abundant alkane in seeps on the deep seafloor. They characterized enzymes involved in the process and found that their reaction breaks an established dogma in the field of anaerobic biochemistry.
-
 News
NewsLyme borreliosis: New approach for developing targeted therapy
A research team has made significant progress in understanding the mechanism of Lyme borreliosis infection and identified a potential way forward for the development of targeted therapies that do not rely on antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsUnnoticeable electric currents could reduce skin infections
Using a few zaps of electricity to the skin, researchers can stop bacterial infections without using any drugs. For the first time, researchers have designed a skin patch that uses imperceptible electric currents to control microbes.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotics and antifungals may slightly affect Parkinson’s risk, study finds
A study has found that people who took multiple courses of penicillin antibiotics had a modestly lower risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, a surprising finding that researchers say highlights the complex relationship between bacteria in the digestive tract and brain health.
-
 News
NewsNative fungus could offer biocontrol for invasive autumn olive
Researchers are studying a native fungus that potentially could kill the invasive autumn olive with minimal human interaction.To remove the autumn olive currently, the plant needs to have its underground root system removed in addition to the destruction of the plant itself, but this fungus could make this process much easier.
-
 News
NewsMaternal antibodies interfere with malaria vaccine responses
Maternal antibodies passed across the placenta can interfere with the response to the malaria vaccine, which would explain its lower efficacy in infants under five months of age, according to research.
-
 News
NewsNew tool enables a more complete and rapid decoding of the language of algal gene expression
A new method that research teams can use to measure and compare different forms of proteins and protein complexes helped reveal a previously unseen molecular signature of how algal genomes are controlled during the cell cycle.
-
 News
NewsMeet the Global Ambassadors: Our Q&A with Matthew B Sullivan
The Microbiologist chats with our new Global Ambassador for the United States, Matthew B Sullivan, who is Professor of Microbiology and Director of the Center of Microbiome Science, at The Ohio State University.
-
 News
NewsPolar bears’ exposure to pathogens is increasing as their environment changes
As the Arctic warms, polar bears now face a greater risk of contracting several pathogens than bears three decades ago, a new study reveals.
-
 News
NewsNovel antibody platform tackles viral mutations
Scientists have developed an innovative antibody platform aimed at tackling one of the greatest challenges in treating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2: their ability to mutate and evade existing vaccines and therapies.
-
 News
NewsStructural biology analysis of a Pseudomonas bacterial virus reveals a genome ejection motor
Bacterial viruses, known as phages, are the most abundant biological entities on the planet and are increasingly used as biomedicines to eradicate antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria.
-
 News
NewsChemists pioneer metallodrug-antibiotic combination strategy to combat superbugs
A combination of different types of antibiotics with bismuth-based drugs, such as Pepto-Bismol, disrupts bacterial iron homeostasis, effectively restoring the bactericidal function of multiple antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsFull-bodied cheese flavor–prediction of flavor development soon possible thanks to new method
Peptides formed during cheese ripening are crucial for the full-bodied flavor of aged cheeses, known as kokumi. Researchers have now developed a new method to analyze these flavor-relevant peptides precisely, quickly, and efficiently.
-
 News
NewsScientists discover how fungi interact with soil actinomycetes
Discovery of a unique microbial interaction offers potential for environmentally friendly control of rice blast disease.
-
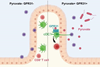 News
NewsStudy reveals how our gut cells detect harmful invaders
Researchers hve found that the GPR31 path in ‘gut surveillance’ cells detects bacterial metabolites and triggers immune responses, opening new possibilities for drug development, vaccines, and probiotics to fight infections.
