All Editorial articles – Page 35
-
 News
NewsCaldic and AmphiStar join forces to transform personal care market in Europe with upcycled microbial biosurfactants
Global distributor Caldic and Belgian biotech innovator AmphiStar have announced an exclusive partnership to distribute and promote AmphiStar’s 100% upcycled microbial biosurfactants for personal care applications across Europe.
-
 News
NewsSummer studentship: Eoin probes medicine-microbiome interactions using in vitro gut model
Eoin McKernan reports back on his AMI-sponsored summer studentship which focused on the relationships between the gut microbiome and the metabolism of variable response drugs.
-
 News
NewsRisk of long COVID in kids doubles after second infection
Children and adolescents were twice as likely to experience long COVID after catching COVID for the second time, compared to their peers with a single previous infection, results running counter to the popular perceptions that COVID in children is ‘mild’.
-
 News
News‘Alarming’ rise in newborn babies with antibiotic-resistant infections, researchers find
Researchers are calling for an urgent overhaul of diagnostic and treatment guidelines for infections in newborn babies, after a study revealed frontline treatments for sepsis are no longer effective to treat the majority of bacterial infections.
-
 News
NewsFriendly soil fungus could replace chemical sprays in battle against crop diseases
A common soil fungus could help farmers reduce their reliance on synthetic fungicides by producing natural airborne chemicals that suppress plant diseases. Trichoderma hamatum releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that inhibit the growth of crop pathogens.
-
 News
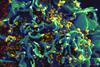
NewsResearchers uncover HIV mystery that could unlock the path to a cure
Researchers have identified for the first time how HIV enters a dormant state in infected cells that allows the virus to “hide” from the immune system and current treatments. HIV orchestrates its own survival by reprogramming host cells to create the perfect hiding place.
-
 News
NewsBiogas slurry boosts biochar’s climate benefits by reshaping soil microbes
A new study finds that pairing biochar with biogas slurry, a nutrient-rich liquid fertilizer from biogas production, can reshape soil microbial communities and significantly alter emissions of carbon dioxide (CO₂), nitrous oxide (N₂O), and methane (CH₄).
-
 News
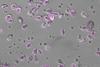
NewsCell death in microalgae resembles that in humans
For the first time, researchers have observed the same type of programmed cell death in microalgae as in humans. The discovery shows that this central biological process is older than previously thought.
-
 News
NewsNew one-hour, low-cost HPV test could transform cervical cancer screening in Africa and beyond
A team of researchers has developed a simple, affordable human papillomavirus (HPV) test that delivers results in less than an hour with no specialized laboratory required.
-
 News
NewsNew clues in how plant microbiomes protect against bacterial speck disease
A new study gives new clues on how a tomato plant’s microbiome can be used to combat the bacterial speck pathogen. Researchers found populations of Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas bacteria on the plants that had developed a resistance against bacterial speck.
-
 News
NewsNatural antimicrobial drugs found in pollen could help us protect bee colonies from infection
Pollen gathered by honeybees contains antimicrobial-producing bacteria that protect the hive against disease, a new study reveals. The same beneficial bacteria occur in pollen stores of honeybee colonies and on pollen of nearby plants.
-
 News
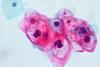
NewsStudy shows HPV vaccine protects vaccinated — and unvaccinated — women
A study has found that the introduction of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine in community settings is highly effective in protecting young women from infections caused by the cervical-cancer-causing virus—including women who didn’t even receive the vaccine.
-
 News
NewsScientists reveal functional RNA splitting mechanism behind origin of Type V CRISPR systems
Researchers have uncovered the molecular innovation that led to the origin of Type V CRISPR-Cas immune systems. Their findings show that the functional splitting of transposon-derived RNAs was the critical innovation driving the emergence of Type V CRISPR-Cas immunity.
-
 News
NewsDeadly pathogens found in commercial raw cat foods
An analysis of commercial raw cat foods detected disease-causing microbes, including some that are resistant to antibiotics, creating risks for both pets and their owners, according to a new study.
-
 News
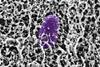
NewsStudy shows mucus contains molecules that block Salmonella infection
Researchers have identified mucins that defend against Salmonella and other bacteria that cause diarrhea. They now hope to mimic this defense system to create synthetic mucins that could help prevent or treat illness in soldiers or other people at risk of exposure to Salmonella.
-
 News
NewsFungal toxin offers colonization support - in small doses
The yeast fungus Candida albicans not only uses the toxin candidalysin to cause infections, but also to colonize the oral mucosa inconspicuously – but only in finely balanced amounts. Too little toxin prevents oral colonization, too much triggers the immune system.
-
 News
NewsSuper-resistant bacteria found in wild birds at a rehabilitation center in Brazil
Researchers have found antibiotic-resistant bacterial clones in wild birds at a rehabilitation center. The identified Escherichia coli clones have been found in community- and hospital-acquired human infections worldwide, and were present in the intestinal tracts of a vulture and an owl.
-
 News
NewsTwo-drug combination shows promise in helping heal chronic wounds
By adding small doses of a simple molecule called chlorate to standard antibiotics, researchers foundthe combination proved 10,000 times more effective at killing bacterial cells in the lab than single-drug antibiotics.
-
 News
NewsGenetic culprits IDed in capture of 100 years of antibiotic resistance evolution
The genetic culprits responsible for the spread of multidrug resistance (MDR) in bacteria have been identified by new research mapping 100 years of bacterial evolution.
-
 News
NewsInactive H5N1 influenza virus in pasteurized milk poses minimal health risks
Proteins and genetic material from H5N1 influenza viruses have been found in pasteurized milk in the United States, but a study shows those inactive viral pieces represent little to no health risk. H5N1-contaminated milk that was pasteurized did not significantly affect the immune system.
