All Editorial articles – Page 3
-
 News
NewsProbiotic may improve sleep quality: new research findings
A recent study has identified a potential new approach to managing sleep disorders. The research focuses on the role of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-producing probiotics in regulating sleep and circadian rhythms.
-
 News
News‘It’s a shot, not a vaccine like MMR’: New skepticism prompts call for action
This ‘vaccine is not a vaccine’ is a new, previously unreported type of vaccine-specific scepticism, and it arose only during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, it might, according to the researchers, also apply to the flu vaccine.
-
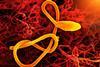 News
NewsScientists zoom in on structure of still lethal Ebola virus
The first high-resolution visualisation of the Ebola virus nucleocapsid provides detailed insights into the interactions within the nucleocapsid complex, unveiling the relationship between molecular interactions and functional regulation.
-
 News
NewsSecurity-relevant research in times of geopolitical polarisation: report
A new report on security-relevant research - including research into pathogens - notes a change within the scientific system due to increased national security interests.
-
 News
NewsBfR organises three-day conference on food microbiology
The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment, the German Society for Microbiology and Hygiene (DGHM) and the Association for General and Applied Microbiology (VAAM) are inviting researchers to the 19th Food Microbiology Conference in Berlin from 1 to 3 April.
-
 News
NewsStudy reveals how dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis exacerbates periodontitis
A new study provides strong evidence that the NOX2/ROS axis plays a key role in the exacerbation of periodontitis in the presence of colitis.
-
 News
NewsSea buckthorn extract exerts anti-free radical, antibacterial and whitening effects on skin
Sea buckthorn flavonoids exhibited excellent antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and whitening effects in a new study. The inhibitory effect of sea buckthorn flavonoids on Propionibacterium acnes were assessed by plate antibacterial assays.
-
 News
NewsProposed cuts to foreign aid could result in millions of HIV deaths, new modelling study estimates
New modelling analysis suggests that proposed funding cuts by major donor countries to foreign aid could undo decades of progress made to end HIV/AIDS as a public health threat and new infections and deaths could surge back to levels not seen since the early 2000s.
-
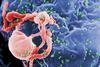
 News
NewsHow Zika virus knocks out our immune defenses
Scientists have made striking discoveries regarding the different infection mechanisms of Zika and dengue virus of the same viral family. These understandings pave the way for vaccine development to combat flaviviruses with similarities.
-
 News
NewsCanada is slowest in reporting bird flu – but COVID shows we can do better
A global study was conducted to measure the reporting speed of pandemic-causing bird flu H5N1 in different countries, among which Canada surprisingly came in last, addressing the need for improvements in the current monitoring procedures.
-
 News
NewsScientists unlock frogs’ antibacterial secrets to combat superbugs
Researchers exploited natural peptides derived from frogs and improved their structural designs as antibiotic candidates, which are effective against complex mock bacterial communities of drug-resistant pathogens in preclinical tests, sparing beneficial microbiota and human cells.
-
 News
NewsResearchers find live hantavirus is carried in various New Mexico small mammal species
A study was carried out to find out the reasons why human cases of the sin nombre hantavirus were concentrated in one particular region of New Mexico, even though the virus was found in 30 species of rodents and small mammals endemic to a different region.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough as researchers discover new class of antibiotics
Researchers have identified a strong candidate to challenge even some of the most drug-resistant bacteria on the planet: a new molecule called lariocidin.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop eco-friendly, nylon-like plastic using microorganisms
Scientists have developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s from glucose derived from biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds.
-
 News
NewsHepatitis B: new rapid diagnostic test to halt mother-to-child transmission
Scientists have assessed a new rapid diagnostic test to identify pregnant women at elevated risk of transmitting hepatitis B to their babies. This diagnostic tool could help eliminate hepatitis B by preventing mother-to-child transmission during childbirth.
-
 News
NewsCorrecting imbalance with the gut microbiota after stroke could reduce brain inflammation
An imbalance in ligands, which are molecules produced by the body and the gut microbiota, can affect a key receptor protein that plays a role in brain inflammation after stroke, according to researchers.
-
 News
NewsMeasles elimination versus eradication: The difference explained
As of March 13, the CDC has confirmed 301 cases of measles as well as the death of a child in Texas. Amira Roess, an epidemiologist and professor of global health, clarifies the benefits of vaccinating children and adolescents against measles.
-
 News
NewsAntibiotic exposure in infancy may boost Type 1 diabetes risk - but microbiota can help
Exposure to antibiotics during a key developmental window in infancy can stunt the growth of insulin-producing cells and may boost risk of diabetes later in life. But the research pinpoints specific microbes that may help those critical cells proliferate in early life.
-
 News
NewsThe gut microbiota-metabolites-brain axis mediates social behavior dysfunction following anaesthesia
New research shows that the anaesthetic Sevoflurane (Sev) influences social functioning via the gut-brain axis, with microbiota-derived bile acids serving as critical mediators in this pathway.
-
 News
NewsTadpoles try to flee dangerous virus in their pond by growing much faster than normal
A new study shows that larvae of wood frogs respond to the presence of a deadly ranavirus by growing and maturing precociously. In response to ranavirus, tadpoles change their growth, development, and resource allocation, which may help them tolerate the energetic demands of infection or escape risky environments to avoid infection.
