All Editorial articles – Page 26
-
 News
NewsWinners of Applied Microbiology International Horizon Awards 2025 announced
The winners of the Applied Microbiology International Horizon Awards 2025 have been announced. The prizes celebrate the brightest minds in the field and promote the research, group, projects, products and individuals who continue to help shape the future of applied microbiology.
-
 News
NewsBruker announces FDA Clearance of Claims 7 and 8 for the MALDI Biotyper® CA System
Bruker has announced FDA clearance of Claim 7 and Claim 8 for its MALDI Biotyper® CA System, marking a significant advancement in clinical microbial identification capabilities.
-
 News
NewsAre there living microbes on Mars? Check the ice, researchers say
By recreating Mars-like conditions in the lab, researchers demonstrated that fragments of the molecules that make up proteins in E. coli bacteria, if present in Mars’ permafrost and ice caps, could remain intact for over 50 million years.
-
 News
NewsSurprising bacteria discovery links Hawaiʻi’s groundwater to the ocean
A new species of bacteria has been discovered off the coast of Oʻahu, shedding light on how unseen microbial life connects Hawaiʻi’s land and sea ecosystems.
-
 News
NewsDual feeding strategy helps Mediterranean coral thrive in rising sea temperatures
An exceptional “dual feeding” strategy underlies a Mediterranean coral’s resilience to rising sea temperatures, according to a study. The stony coral Oculina patagonica is known to feed itself with or without algae.
-
 News
NewsMiniature noses to help prevent infections and promote nasal health
To better understand how different bacteria interact with the lining of the human nose, researchers used a miniature model of the human nose to study how bacteria can live in nasal passages.
-
 News
NewsEngineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industries
Their system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.
-
 News
NewsNew antivirals could help prevent cold sores by changing cell structures
A class of antivirals called Pin1 inhibitors could reduce or stop outbreaks of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), the common infection behind oral herpes, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsIn the midst of a global dengue epidemic, Wolbachia kept a Brazilian city safe
In the middle of the world’s worst global dengue epidemic, a city in Brazil was effectively protected by an innovative program that introduced the bacterium Wolbachia into the local mosquito population, lowering the rate of dengue by almost 90 per cent.
-
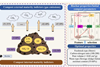 News
NewsGlobal analysis reveals how biochar supercharges composting and cuts greenhouse gases
By analyzing data from 125 studies across the world, researchers showed that adding biochar to composting systems significantly boosts compost quality while slashing harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
-
 News
News1000-litre ‘corn-to-carrier’ demo turns stover into 10.6 g L⁻¹ microbial lipids
Researchers have shown that last autumn’s corn stalks can be transformed into a palm-oil-like fat suitable for aviation biofuel or cosmetics without the energy-guzzling steps that have kept lignocellulosic biorefineries on the drawing board.
-
 News
NewsNew monoclonal antibody shows promise for preventing malaria infections
A new early-stage clinical trial has found that a novel monoclonal antibody provided dose-dependent full protection against the malaria parasite with minimal side effects.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sparks immune response to fight cancer
Patients with advanced lung or skin cancer who received a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine within 100 days of starting immunotherapy drugs lived significantly longer than those who did not get the vaccine, researchers have found.
-
 News
NewsAll-in-one POM-based nanoreactor with oxidase-like activity for versatile detection and antibacterial action
A research team has developed a novel nanoreactor that enables dual-mode biomarker detection and effective antibacterial treatment.
-
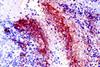 News
NewsStudy reveals how bacteria in tumors drive treatment resistance in cancer
Researchers have uncovered a previously unknown way for microbes within tumors to contribute to treatment resistance in certain cancers. The study finds these microbes push cancer cells into a reversible resting state, allowing them to become resistant to certain chemotherapies.
-
 News
NewsScientist wins research grant to create mucin-on-a-chip for IBD research
Dr. Ilana Kolodkin-Gal of the Scojen Institute for Synthetic Biology has won a research grant from the BSF-NSF to investigate the role of invasive and pathogenic strains of intestinal bacteria in disrupting the integrity of the intestinal barrier.
-
 News
NewsStinkbug leg organ contains symbiotic fungi to shield eggs from parasitic wasps
What looked like a hearing organ on a tiny stinkbug’s leg turned out to be something far stranger: a fungal nursery that mother bugs use to coat their newly laid eggs in protective symbiotic hyphae, shielding their offspring from parasitic wasps.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome affects alcohol preference by influencing brain’s reward system
A new study shows how an overgrowth of Candida albicans - overly abundant in people with alcohol use disorder - increases levels of inflammatory molecules that can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect the desire for alcohol.
-
 News
NewsAnts alter their nest networks to prevent epidemics, study finds
Ants make a series of clever architectural adjustments to their nests to prevent the spread of disease, new research has found. Nests built by colonies exposed to disease had far more widely spread entrances and were more separated, with fewer direct connexions between chambers.
-
 News
NewsAfrican wildlife poop sheds light on what shapes the gut ecosystem
A study of elephants, giraffes and other wildlife in Namibia’s Etosha National Park underscores the ways in which the environment, biological sex, and anatomical distinctions can drive variation in the gut microbiomes across plant-eating species.
