All Editorial articles – Page 166
-
 News
NewsOxygen vacancy boosting Fenton reaction helps to fight bacterial infection in bone scaffold
A groundbreaking approach to address bacterial infection in artificial bone transplantation works by enriching H2O2 from the microenvironment and amplifying the ability of Fenton reaction to functionalize bone scaffold with antibacterial properties.
-
 News
NewsGut fungi trigger long-lasting severe COVID-19 immune response
Researchers have found that the growth of fungi in the intestinal tract, particularly strains of Candida albicans yeast, trigger an upsurge in immune cells whose actions can exacerbate lung damage.
-
 News
NewsClimate change is increasing risk of high toxin concentrations in Northern US lakes
As climate change warms the Earth, higher-latitude regions will be at greater risk for toxins produced by algal blooms, with water temperatures of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius at greatest risk for developing dangerous levels of a common algae-produced toxin.
-
 News
NewsSoft, living materials made with algae glow under stress
A team of researchers has developed soft yet durable materials that glow in response to mechanical stress, such as compression, stretching or twisting, and deriving their luminescence from single-celled algae known as dinoflagellates.
-
 News
NewsLactate-producing bacteria inside tumors promote resistance to radiation therapy
Researchers have discovered that lactate-producing intratumoral bacteria drives resistance to radiation therapy, suggesting that lactic acid-producing bacteria present in various cancers may serve as novel therapeutic targets.
-
 News
NewsOral pathogen increases heart attack damage
Researchers have found that a periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, inhibits autophagosome–lysosome fusion, and can therefore worsen cardiac remodeling and cause cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction.
-
 News
NewsStudy supports potential for injectable ‘chemical vaccine’ for malaria using atovaquone
Researchers demonstrate in mouse model that key mutation that renders malaria parasites resistant to atovaquone also makes them non-transmissible via mosquitoes.
-
 News
NewsBroad-spectrum antiviral candidate targets dengue and SARS-CoV-2
A broad-spectrum antiviral drug candidate, 2-thiouridine, that targets positive-strand RNA viruses has been identified and characterized.
-
 News
NewsTechnique restores the function of a human cell surface protein in yeast cells
Scientists report a technique that could promote the use of yeast as a convenient platform to study human proteins and develop new drugs.
-
 News
NewsSoil carried on sea freight loaded with dangerous plant diseases
Soil collected from the external surfaces of sea freight was found to support live microorganisms, worms, seeds and insects,, confirming that shipping containers provide a pathway for the movement of exotic species.
-
 News
NewsAntimicrobial peptides modulate lung injury by altering the intestinal microbiota
Researchers have identified a gut-lung axis driven by intestinal antimicrobial peptide expression and mediated by the intestinal microbiota that is linked to lung injury in newborns.
-
 News
NewsSpaceflight could alter behaviour of human microbiome, bobtail squid study suggests
Microgravity changes how effectively symbiotic bacteria colonise the light organ of the bobtail squid, according to a new study which has implications for how the human microbiome may respond to spaceflight. Source: Joseph Emhof Bobtail squid just after hatching The research by a University of Florida team, ...
-
 News
NewsDeep dive into the gut unlocks new disease treatments
Researchers say it’s not only possible to map just what species are in the gut microbiome but how they interact and how that can affect the whole body.
-
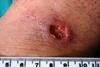 News
NewsGenetic fingerprint suggests cutaneous leishmaniasis may be gaining foothold in US
Analysis reveals DNA evidence of a US-acquired strain of cutaneous leishmaniasis - the prospect of a growing threat comes amidst concerns that domestic sand flies could acquire a deadly form of the disease via dog imports.
-
 News
News‘Subway map’ of Lyme disease pathways IDs potential treatment targets
Researchers have developed a genome-scale metabolic model of key metabolic activities of the bacterium that causes Lyme disease, successfully identifying two compounds that selectively target routes only used by Lyme disease to infect a host.
-
 News
NewsResearchers discover associations among PTSD, diet, and the gut microbiome
A new study suggests that adhering to a Mediterranean diet may alleviate or prevent posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms.
-
 News
NewsTwo probiotics identified as promising hypertension treatments
A study has added 2 new strains to the list of potential antihypertensive probiotics. In experiments on hypertensive mice, treatment with Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus returned blood pressure to normal levels.
-
 News
NewsYeast speeds discovery of medicinal compounds in plants
Researchers have harnessed the power of baker’s yeast to create a cost-effective and highly efficient approach for unraveling how plants synthesize medicinal compounds, and used the new method to identify key enzymes in a kratom tree.
-
 News
NewsResearchers probe >10,000 drug combinations to beat AMR
In an extensive investigation, researchers have tested over 10,000 drug combinations against some of the leading pathogenic bacteria carrying antimicrobial resistance and causing mortality.
-
 News
NewsPromising results from E coli-produced HPV vaccine trials in female volunteers
Researchers conducting human trials of an E. coli-produced 9-valent HPV vaccine candidate found it was well tolerated and immunogenic, warranting further efficacy studies in larger populations.
