All COVID-19 articles – Page 22
-
 News
NewsDUV LEDs offer rapid inactivation of human respiratory RNA viruses
A deep ultraviolet LED based on AlGaN, whose wavelength is tunable from 365 to 210 nm, is a perfect alternative to mercury lamps to inactivate human respiratory RNA viruses due to its pollution-free, small-size and energy-conservation qualities.
-
 News
NewsHeart drug peruvoside could prevent spread of up to 12 viruses
Peruvoside, a plant-based compound that is commonly used to treat heart failure, has been discovered to be able to prevent up to 12 medically important viruses, all originating from different virus families.
-
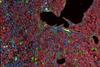 News
NewsEngineered lung cells light up when Covid sparks immune response
Scientists have engineered lab-grown lung epithelial cells to light up red in colour once they launch an immune response, creating a tool that can be used to screen for drugs that can help treat COVID-19 and other emerging infections.
-
 News
NewsResearchers develop adhesive bandage that can detect COVID-19 antibodies
Researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi have developed a new rapid testing method for COVID-19 – an adhesive bandage that relies on gold nanoparticles to quickly detect the immune antibodies in the bloodstream. These antibodies, named IgM and IgG, are naturally produced as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection, ...
-
 News
NewsNewer Covid strains are less capable of surviving in the air
Scientists investigating why airborne viruses lose their infectivity have revealed how cleaner air kills the virus significantly quicker and why opening a window may be more important than originally thought.
-
 News
NewsVirologist receives British Empire Medal for pandemic communications
Virologist Dr Naomi Forrester-Soto from Keele University has received a British Empire Medal (BEM) in the inaugural King’s Birthday Honours list for services to public communication during the Covid-19 pandemic.
-
 News
NewsBCG vaccine found ineffective against COVID-19 in healthcare workers
An international trial investigating the potential immune-boosting effects of the tuberculosis BCG vaccine against COVID-19 found that the risk of developing the disease during the first six months after vaccination was not reduced in participants as originally hoped for.
-
 News
NewsHighly infective Covid virus needs only a single door opener
Researchers have provided evidence that a single virus binds to a single receptor, opening the door for a highly efficient infection.
-
 News
NewsCovid-19 jab shows no serious side effects in young children
A review of more than 245,000 doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines given to young children - most of them aged 4 and younger - found no indications of serious side effects.
-
 News
NewsCats can play a role in family transmission of COVID-19
Cats can play a role in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and their contaminated environment can be infectious, according to new research.
-
 Opinion
OpinionThe threat of viral zoonosis hasn’t gone away
Why we’re liable to be ambushed by viral zoonosis - despite everything we’ve learned from Covid
-
 News
NewsCovid beta variant in Mozambique transmitted through regional migration
A genomic surveillance study in Mozambique reveals that the beta variant of the virus was transmitted through regional migration, and questions the benefits of closing borders.
-
 News
NewsLaser breathalyzer sniffs out COVID in real time
Scientists have made an important leap forward in the quest to diagnose disease using exhaled breath, reporting that a new laser-based breathalyzer powered by artificial intelligence (AI) can detect COVID-19 in real-time with excellent accuracy.
-
 News
NewsConcerns raised over popular Covid disinfectants
The Covid-19 pandemic has boosted the unnecessary use of antimicrobial chemicals linked to health problems, antimicrobial resistance, and environmental harm, scientists warn.
-
 News
NewsAlgorithm boosts Covid vaccine response 128-fold
Researchers have developed an AI algorithm that can rapidly design highly stable COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sequences that were previously unattainable, achieving a 128-fold increase in the vaccine’s antibody response.
-
 News
NewsFitness landscape explains Covid variant origins
Researchers have uncovered the mechanisms behind the emergence of new and dangerous coronavirus variants, such as Alpha, Delta, Omicron, and others.
-
 News
NewsMonoclonal antibody programme targets mucormycosis
Vitalex Biosciences has been awarded an SBIR Phase 2 grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) at the National Institutes of Health for VX-01, a monoclonal antibody (mAB) programme targeting the debilitating indication of the fungal disease, mucormycosis.
-
 News
NewsBCG does not protect health workers against Covid
A world-leading international trial into the immune boosting benefits of the tuberculosis vaccine, BCG, has found it does not protect healthcare workers against COVID-19.
-
 News
NewsSystem targets and degrades viral RNA to treat Covid infection
Researchers have developed a system that directly targets and degrades the viral RNA genome, reducing infection in mice. The method could be adapted to fight off many viruses, as well as treat various diseases.
-
 News
NewsStudy of Covid contamination of shipping materials may yield guidance for goods transportation
Researchers investigating how environmental factors affect the persistence of two different, highly transmissible Omicron variants on shipping materials find that viability depends on the type of surface, the temperature and the original viral concentration.
