All Bacteria articles – Page 5
-
 News
NewsSnakebites: COVID vaccine tech could limit venom damage
The same technology used in COVID-19 vaccines could help prevent muscle damage from snakebites, according to scientists who say it could be even more useful for other conditions where toxins cause harm gradually, such as blocking harmful toxins produced by bacteria during infections.
-
 News
NewsNatural, non-engineered bacterium selectively targets colorectal cancer
Scientists have demonstrated that the marine bacterium Photobacterium angustum exhibits potent antitumor effects against colorectal cancer. The natural bacterium requires no genetic modification yet selectively accumulates in tumor tissues with minimal impact on healthy organs.
-
 News
NewsTeam discovers cyanobacteria activate different genes by day and by night
By analyzing gene expression in the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme, scientists discovered that during daylight, the cells focus on metabolism. But under cover of darkness, they turn to the control of genome repair and activate various genetic elements.
-
 News
NewsResearchers subvert plasmids to combat antibiotic resistance
Scientists have devised a way to track the evolution and spread of antibiotic resistance in individual bacteria by measuring competition among plasmids. Plasmids evolve independently but also help drive bacterial evolution, including the development of resistance to antimicrobial compounds. They are the primary way that resistance can jump from one type of bacteria to another.
-
 News
NewsToxic gut bacteria may drive ulcerative colitis by killing protective immune cells
A toxin-secreting gut bacterium may fuel ulcerative colitis by killing protective immune cells that maintain intestinal homeostasis, according to a new study. The findings suggest potential for new treatment strategies.
-
 News
NewsMicrobial nano-selenium breakthrough boosts tea quality and safety
Scientists developing selenium-enriched tea have identified a powerful selenium-reducing bacterium, Raoultella ornithinolytica S-1, capable of converting inorganic selenium into selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) while simultaneously promoting plant growth.
-
 News
NewsNew study finds higher levels of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in surface water during winter
A new study has found that the levels of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) present in surface water increase during winter. Flooding, sewer overflows and agricultural run-off all contribute to a cocktail of pollutants that can increase AMR genes in surface water, potentially turning regular bugs into ‘superbugs’.
-
 News
NewsDiphtheria toxin fragment harnessed to fuse lipid vesicles at neutral pH
Researchers have discovered a novel way to fuse lipid vesicles at neutral pH. By harnessing a fragment of the diphtheria toxin, the team achieved vesicle membrane fusion without the need for pre-treatment or harsh conditions, opening the door to new applications.
-
 News
NewsScientists develop world’s first modular co-culture platform for the one-pot production of rainbow-colored bacterial cellulose
The team engineered Komagataeibacter xylinus for bacterial cellulose synthesis and Escherichia coli for natural colorant overproduction. A co-culture of these engineered strains enabled the in situ coloration of bacterial cellulose.
-
 News
NewsScientists use computer model to improve hospitals’ ability to limit spread of drug-resistant infections
The computer model improves on traditional methods like contact tracing by inferring asymptomatic carriers in the spread of antibiotic-resistant infections.
-
 News
NewsDrinking water people believe to be safe and clean often contain potentially dangerous bacteria
A study in Guatemala found the sources of drinking water people believe to be safe and clean often contain potentially dangerous bacteria. Bottled water sold in large refillable jugs was the most frequently contaminated with coliform bacteria – an indicator of fecal contamination.
-
 News
NewsStudy unveils structure, identification and characterization of the RibD-enolase complex in Francisella
A study aiming to identify anti-tularemia drug targets determined the atomic structure and identified its components of the native RibD-enolase protein complex in Francisella novicida.
-
 News
NewsNew nanogel technology destroys drug-resistant bacteria in hours
A novel technology shows over 99.9% effectiveness against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa). It centres on a heteromultivalent nanogel: a flexible particle made by crosslinking polymers and adding sugar residues (galactose and fucose) alongside antimicrobial peptides.
-
 News
NewsBacteria ‘pills’ could detect gut diseases — without the endoscope
Researchers report that they’ve developed a sensor made of tiny microspheres packed with blood-sensing bacteria that detect markers of gastrointestinal disease. Taken orally, the miniature “pills” also contain magnetic particles that make them easy to collect from stool. Excreted from mouse models with colitis, the bacterial sensor detected gastrointestinal bleeding within minutes.
-
 News
NewsGSK and Fleming Initiative scientists unite to target AMR with advanced AI
GSK and the Fleming Initiative have announced six major new research programmes, called ‘Grand Challenges’ which harness some of the best scientific expertise and the latest technologies, including advanced AI, to find new ways to slow the progress of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
-
 News
NewsProbiotic bifidobacterium may boost cancer treatment and suppress tumors
A new review explores how bifidobacterium, a common probiotic found in the gut, may contribute to cancer prevention and therapy. The authors highlight the growing importance of gut health in cancer treatment and shed light on how bifidobacterium could complement standard cancer therapies.
-
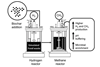 News
NewsBiochar boosts clean energy output from food waste in novel two-stage digestion system
A new study from researchers at the University of Western Australia and Universitas Brawijaya has found that adding biochar to advanced food waste recycling systems can significantly increase the clean energy yields of hydrogen and methane. This breakthrough offers promising strategies for municipalities and industries aiming to turn food scraps ...
-
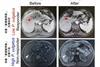 News
NewsGut bacterium impairs liver cancer treatment, inducing immunotherapy resistance
Researchers discovered that transplanting the gut bacterium Phocaeicola vulgatus into mouse models of liver cancer induced immunotherapy resistance. The finding is consistent with clinical observations in patients, showing that patients with low levels of P. vulgatus responded better to treatment.
-
 News
NewsManure digesters on farms carry limited benefits and potential harms
Manure digesters, touted as eco-friendly solutions for managing agricultural waste and reducing greenhouse gases, have limited capacity to reduce livestock-related greenhouse gas emissions, and entail potential hazards that may outweigh their benefits.
-
 News
NewsScientist who harnesses bacteria to deliver green solutions is winner in 2025 Tata Transformation Prize
A scientist who harnesses bacteria to deliver green solutions has been named as one of the winners of the 2025 Tata Transformation Prize. Balasubramanian Gopal, PhD, Indian Institute of Science, has been named Sustainability Winner in the awards.
